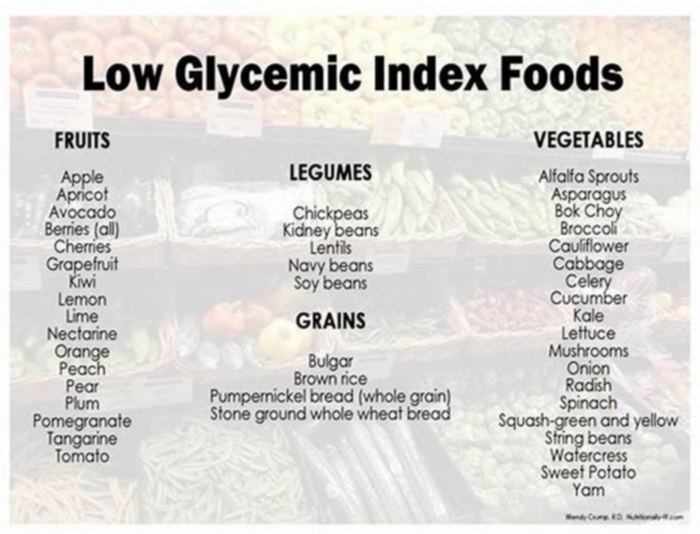
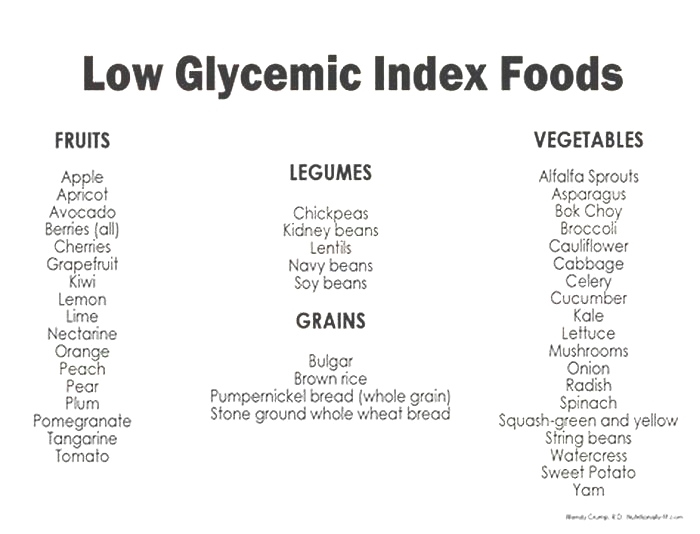
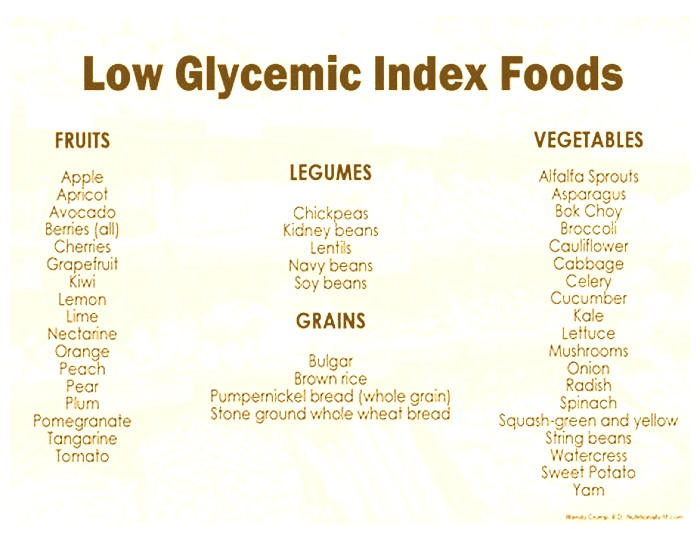
Which food has the lowest glycemic load
Micronutrient Information Center
1.Liu S, Willett WC. Dietary glycemic load and atherothrombotic risk. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2002;4(6):454-461.
2.Brouns F, Bjorck I, Frayn KN, et al. Glycaemic index methodology. Nutr Res Rev. 2005;18(1):145-171. (PubMed)
3.Augustin LS, Kendall CW, Jenkins DJ, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load and glycemic response: An International Scientific Consensus Summit from the International Carbohydrate Quality Consortium (ICQC). Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015;25(9):795-815. (PubMed)
4.Monro JA, Shaw M. Glycemic impact, glycemic glucose equivalents, glycemic index, and glycemic load: definitions, distinctions, and implications. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(1):237S-243S. (PubMed)
5. The University of Sydney. About Glycemic Index. Available at: https://glycemicindex.com/about-gi/. Accessed 1/4/22.
6. The International Organization for Standardization. Food products - Determination of the glycaemic index (GI) and recommendation for food classification. 2016. Available at: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:26642:ed-1:v1:en. Accessed 2/22/16.
7.Ludwig DS. The glycemic index: physiological mechanisms relating to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. JAMA. 2002;287(18):2414-2423. (PubMed)
8.Willett WC. Eat, Drink, and be Healthy: The Harvard Medical School Guide to Healthy Eating. New York: Simon & Schuster; 2001.
9.Dodd H, Williams S, Brown R, Venn B. Calculating meal glycemic index by using measured and published food values compared with directly measured meal glycemic index. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94(4):992-996. (PubMed)
10.Silva FM, Kramer CK, Crispim D, Azevedo MJ. A high-glycemic index, low-fiber breakfast affects the postprandial plasma glucose, insulin, and ghrelin responses of patients with type 2 diabetes in a randomized clinical trial. J Nutr. 2015;145(4):736-741. (PubMed)
11.Ranawana V, Leow MK, Henry CJ. Mastication effects on the glycaemic index: impact on variability and practical implications. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014;68(1):137-139. (PubMed)
12.Sun L, Ranawana DV, Tan WJ, Quek YC, Henry CJ. The impact of eating methods on eating rate and glycemic response in healthy adults. Physiol Behav. 2015;139:505-510. (PubMed)
13.Venn BS, Williams SM, Mann JI. Comparison of postprandial glycaemia in Asians and Caucasians. Diabet Med. 2010;27(10):1205-1208. (PubMed)
14.Wolever TM, Jenkins AL, Vuksan V, Campbell J. The glycaemic index values of foods containing fructose are affected by metabolic differences between subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2009;63(9):1106-1114. (PubMed)
15.Goff LM, Cowland DE, Hooper L, Frost GS. Low glycaemic index diets and blood lipids: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23(1):1-10. (PubMed)
16.Willett W, Manson J, Liu S. Glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76(1):274S-280S. (PubMed)
17.Gross LS, Li L, Ford ES, Liu S. Increased consumption of refined carbohydrates and the epidemic of type 2 diabetes in the United States: an ecologic assessment. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;79(5):774-779. (PubMed)
18.Bhupathiraju SN, Tobias DK, Malik VS, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of type 2 diabetes: results from 3 large US cohorts and an updated meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;100(1):218-232. (PubMed)
19.Mosdol A, Witte DR, Frost G, Marmot MG, Brunner EJ. Dietary glycemic index and glycemic load are associated with high-density-lipoprotein cholesterol at baseline but not with increased risk of diabetes in the Whitehall II study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86(4):988-994. (PubMed)
20.Sahyoun NR, Anderson AL, Tylavsky FA, et al. Dietary glycemic index and glycemic load and the risk of type 2 diabetes in older adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(1):126-131. (PubMed)
21.Sakurai M, Nakamura K, Miura K, et al. Dietary glycemic index and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in middle-aged Japanese men. Metabolism. 2012;61(1):47-55. (PubMed)
22.Sluijs I, Beulens JW, van der Schouw YT, et al. Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, and digestible carbohydrate intake are not associated with risk of type 2 diabetes in eight European countries. J Nutr. 2013;143(1):93-99. (PubMed)
23.van Woudenbergh GJ, Kuijsten A, Sijbrands EJ, Hofman A, Witteman JC, Feskens EJ. Glycemic index and glycemic load and their association with C-reactive protein and incident type 2 diabetes. J Nutr Metab. 2011;2011:623076. (PubMed)
24.Villegas R, Liu S, Gao YT, et al. Prospective study of dietary carbohydrates, glycemic index, glycemic load, and incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in middle-aged Chinese women. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(21):2310-2316. (PubMed)
25.Greenwood DC, Threapleton DE, Evans CE, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load, carbohydrates, and type 2 diabetes: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(12):4166-4171. (PubMed)
26.Livesey G, Taylor R, Livesey H, Liu S. Is there a dose-response relation of dietary glycemic load to risk of type 2 diabetes? Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;97(3):584-596. (PubMed)
27.Dyson PA, Kelly T, Deakin T, et al. Diabetes UK evidence-based nutrition guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes. Diabet Med. 2011;28(11):1282-1288. (PubMed)
28.Mann JI, De Leeuw I, Hermansen K, et al. Evidence-based nutritional approaches to the treatment and prevention of diabetes mellitus. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2004;14(6):373-394. (PubMed)
29.American Diabetes Association. 4. Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2016;39 Suppl 1:S36-38. (PubMed)
30.Ma XY, Liu JP, Song ZY. Glycemic load, glycemic index and risk of cardiovascular diseases: meta-analyses of prospective studies. Atherosclerosis. 2012;223(2):491-496. (PubMed)
31.Dong JY, Zhang YH, Wang P, Qin LQ. Meta-analysis of dietary glycemic load and glycemic index in relation to risk of coronary heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2012;109(11):1608-1613. (PubMed)
32.Fan J, Song Y, Wang Y, Hui R, Zhang W. Dietary glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and stroke mortality: a systematic review with meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52182. (PubMed)
33.Mirrahimi A, de Souza RJ, Chiavaroli L, et al. Associations of glycemic index and load with coronary heart disease events: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohorts. J Am Heart Assoc. 2012;1(5):e000752. (PubMed)
34.Turati F, Dilis V, Rossi M, et al. Glycemic load and coronary heart disease in a Mediterranean population: the EPIC Greek cohort study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015;25(3):336-342. (PubMed)
35.Liu S, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, et al. A prospective study of dietary glycemic load, carbohydrate intake, and risk of coronary heart disease in US women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71(6):1455-1461. (PubMed)
36.Beulens JW, de Bruijne LM, Stolk RP, et al. High dietary glycemic load and glycemic index increase risk of cardiovascular disease among middle-aged women: a population-based follow-up study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;50(1):14-21. (PubMed)
37.Cai X, Wang C, Wang S, et al. Carbohydrate intake, glycemic index, glycemic load, and stroke: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2015;27(5):486-496. (PubMed)
38.Rossi M, Turati F, Lagiou P, Trichopoulos D, La Vecchia C, Trichopoulou A. Relation of dietary glycemic load with ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: a cohort study in Greece and a meta-analysis. Eur J Nutr. 2015;54(2):215-222. (PubMed)
39.Buscemi S, Cosentino L, Rosafio G, et al. Effects of hypocaloric diets with different glycemic indexes on endothelial function and glycemic variability in overweight and in obese adult patients at increased cardiovascular risk. Clin Nutr. 2013;32(3):346-352. (PubMed)
40.Bullo M, Casas R, Portillo MP, et al. Dietary glycemic index/load and peripheral adipokines and inflammatory markers in elderly subjects at high cardiovascular risk. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23(5):443-450. (PubMed)
41.Liu S, Manson JE, Buring JE, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Ridker PM. Relation between a diet with a high glycemic load and plasma concentrations of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in middle-aged women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;75(3):492-498. (PubMed)
42.Jones JL, Park Y, Lee J, Lerman RH, Fernandez ML. A Mediterranean-style, low-glycemic-load diet reduces the expression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase in mononuclear cells and plasma insulin in women with metabolic syndrome. Nutr Res. 2011;31(9):659-664. (PubMed)
43.Turati F, Galeone C, Gandini S, et al. High glycemic index and glycemic load are associated with moderately increased cancer risk. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015;59(7):1384-1394. (PubMed)
44.Aune D, Chan DS, Lau R, et al. Carbohydrates, glycemic index, glycemic load, and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control. 2012;23(4):521-535. (PubMed)
45.Choi Y, Giovannucci E, Lee JE. Glycaemic index and glycaemic load in relation to risk of diabetes-related cancers: a meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. 2012;108(11):1934-1947. (PubMed)
46.Mulholland HG, Murray LJ, Cardwell CR, Cantwell MM. Glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of digestive tract neoplasms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89(2):568-576. (PubMed)
47.Mullie P, Koechlin A, Boniol M, Autier P, Boyle P. Relation between breast cancer and high glycemic index or glycemic load: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2016;56(1):152-159. (PubMed)
48.Tsai CJ, Leitzmann MF, Willett WC, Giovannucci EL. Dietary carbohydrates and glycaemic load and the incidence of symptomatic gall stone disease in men. Gut. 2005;54(6):823-828. (PubMed)
49.Tsai CJ, Leitzmann MF, Willett WC, Giovannucci EL. Glycemic load, glycemic index, and carbohydrate intake in relation to risk of cholecystectomy in women. Gastroenterology. 2005;129(1):105-112. (PubMed)
50.Wang Q, Xia W, Zhao Z, Zhang H. Effects comparison between low glycemic index diets and high glycemic index diets on HbA1c and fructosamine for patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes. 2015;9(5):362-369. (PubMed)
51.Evert AB, Boucher JL. New diabetes nutrition therapy recommendations: what you need to know. Diabetes Spectr. 2014;27(2):121-130. (PubMed)
52.Evert AB, Boucher JL, Cypress M, et al. Nutrition therapy recommendations for the management of adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014;37 Suppl 1:S120-143. (PubMed)
53.Louie JC, Markovic TP, Perera N, et al. A randomized controlled trial investigating the effects of a low-glycemic index diet on pregnancy outcomes in gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(11):2341-2346. (PubMed)
54.Louie JC, Markovic TP, Ross GP, Foote D, Brand-Miller JC. Effect of a low glycaemic index diet in gestational diabetes mellitus on post-natal outcomes after 3 months of birth: a pilot follow-up study. Matern Child Nutr. 2015;11(3):409-414. (PubMed)
55.Markovic TP, Muirhead R, Overs S, et al. Randomized controlled trial investigating the effects of a low-glycemic index diet on pregnancy outcomes in women at high risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: The GI Baby 3 Study. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(1):31-38. (PubMed)
56.Flegal KM, Kit BK, Orpana H, Graubard BI. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2013;309(1):71-82. (PubMed)
57.Kopelman P. Health risks associated with overweight and obesity. Obes Rev. 2007;8 Suppl 1:13-17. (PubMed)
58.Hu T, Mills KT, Yao L, et al. Effects of low-carbohydrate diets versus low-fat diets on metabolic risk factors: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Am J Epidemiol. 2012;176 Suppl 7:S44-54. (PubMed)
59.Shyam S, Arshad F, Abdul Ghani R, Wahab NA. Low glycaemic index diets improve glucose tolerance and body weight in women with previous history of gestational diabetes: a six months randomized trial. 2013;12:68. (PubMed)
60.Ebbeling CB, Leidig MM, Feldman HA, Lovesky MM, Ludwig DS. Effects of a low-glycemic load vs low-fat diet in obese young adults: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2007;297(19):2092-2102. (PubMed)
61.Klemsdal TO, Holme I, Nerland H, Pedersen TR, Tonstad S. Effects of a low glycemic load diet versus a low-fat diet in subjects with and without the metabolic syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010;20(3):195-201. (PubMed)
62.Juanola-Falgarona M, Salas-Salvado J, Ibarrola-Jurado N, et al. Effect of the glycemic index of the diet on weight loss, modulation of satiety, inflammation, and other metabolic risk factors: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;100(1):27-35. (PubMed)
63.Schwingshackl L, Hoffmann G. Long-term effects of low glycemic index/load vs. high glycemic index/load diets on parameters of obesity and obesity-associated risks: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23(8):699-706. (PubMed)
64.Ludwig DS. Dietary glycemic index and the regulation of body weight. Lipids. 2003;38(2):117-121. (PubMed)
65.Lennerz BS, Alsop DC, Holsen LM, et al. Effects of dietary glycemic index on brain regions related to reward and craving in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;98(3):641-647. (PubMed)
66.Aller EE, Larsen TM, Claus H, et al. Weight loss maintenance in overweight subjects on ad libitum diets with high or low protein content and glycemic index: the DIOGENES trial 12-month results. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014;38(12):1511-1517. (PubMed)
67.Wadden TA, Webb VL, Moran CH, Bailer BA. Lifestyle modification for obesity: new developments in diet, physical activity, and behavior therapy. Circulation. 2012;125(9):1157-1170. (PubMed)
68.Atkinson FS, Foster-Powell K, Brand-Miller JC. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values: 2008. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(12):2281-2283. (PubMed)