What is the lowest GI rice

Low-Gi Rice Options for Diabetics: Healthy Choices
People with diabetes often question whether rice can be a part of their diet. However, including a suitable variety of rice in a diabetic meal plan can help in managing blood sugar levels. Rice is a high-energy food that is packed with nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and fiber. While white rice has a high glycemic index and should be avoided, there are several low-Gi rice options that can be beneficial for diabetics. These options include brown rice, whole grain basmati rice, red rice, black rice, wild rice, and more. By choosing these low-Gi rice varieties and following certain cooking techniques, people with diabetes can enjoy rice as part of a healthy diet.
Key Takeaways
- Including suitable rice varieties in a diabetic meal plan can help manage blood sugar levels.
- White rice should be avoided due to its high glycemic index.
- Low-Gi rice options for diabetics include brown rice, whole grain basmati rice, red rice, black rice, and wild rice.
- Following proper cooking techniques can further reduce the impact of rice on blood sugar levels.
- Rice can be a beneficial and healthy part of a diabetic diet when chosen and prepared correctly.
The Nutritional Profile of Rice
Rice is not just a staple food; it is also a nutrient powerhouse. It is a great source of energy, providing around 345 calories per 100 grams. Rice is cholesterol-free and contains various vitamins and minerals, including:
- Calcium: Essential for strong bones and teeth
- Potassium: Helps regulate blood pressure
- Iron: Important for oxygen transport in the body
- Phosphorus: Supports healthy bones and teeth
Rice is also rich in riboflavin, niacin, and thiamine, which have been associated with preventing certain forms of cancer, Alzheimers disease, and heart disease.
However, it is important to note that the polishing process can strip rice of its nutrients, particularly the fiber content. This is why unpolished rice, such as brown rice and whole grain basmati rice, are better choices for people with diabetes.
Explore the nutritional profile of rice below in this comprehensive table:

| Nutrient | Content per 100g |
|---|---|
| Calories | 345 kcal |
| Protein | 6.6g |
| Fat | 0.7g |
| Carbohydrates | 77.5g |
| Fiber | 1.3g |
| Calcium | 28mg |
| Potassium | 115mg |
| Iron | 0.8mg |
| Phosphorus | 110mg |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | 0.05mg |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) | 1.6mg |
| Thiamine (Vitamin B1) | 0.17mg |
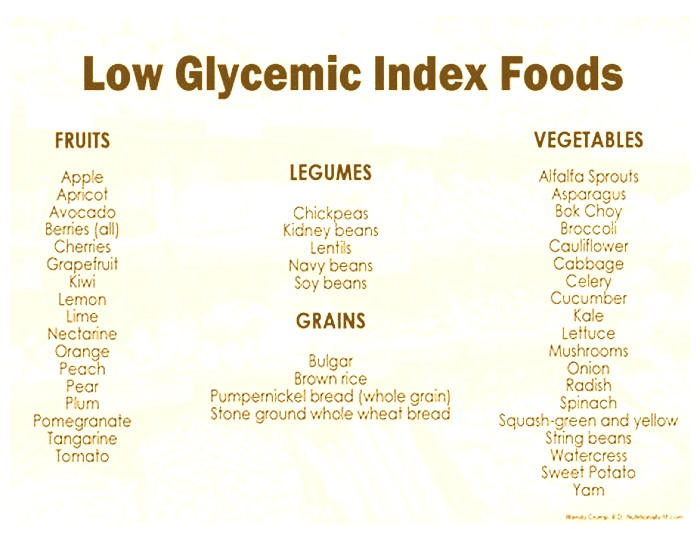
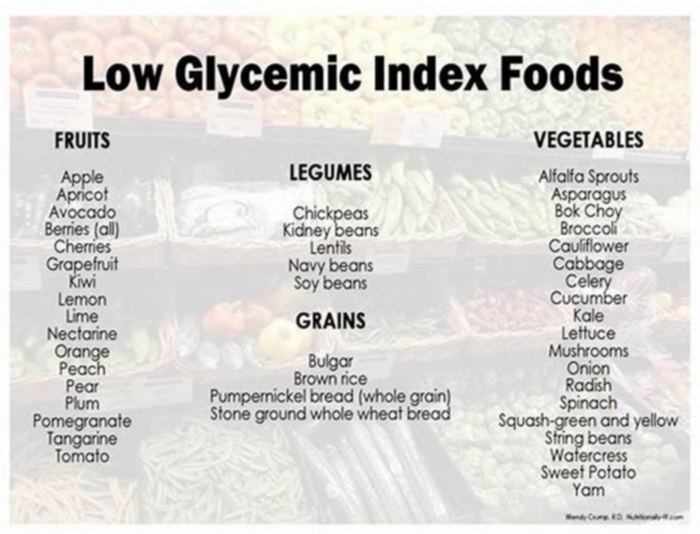
Low-Gi Rice Varieties for Diabetics
When it comes to choosing rice varieties for diabetics, it is important to consider the glycemic index (GI) of the rice. The glycemic index measures the impact of a food on blood sugar levels. Lower-Gi rice varieties take longer to digest and release sugars into the bloodstream slowly, making them a better choice for diabetics.
Some notable low-Gi rice options include:
| Rice Variety | Glycemic Index (GI) |
|---|---|
| Brown Rice | 50-55 |
| Whole Grain Basmati Rice | 50-52 |
| Red Rice | Around 55 |
| Black Rice | 42-45 |
| Wild Rice | 45 |
These low-Gi rice varieties can help in managing blood sugar levels effectively. Incorporating them into a diabetic meal plan provides a delicious and nutritious option.

Adding variety to meals is important, especially for individuals with diabetes. The following section will explore some alternative low-Gi options to white rice.
Cooking Techniques for Lowering the Glycemic Index
The method of cooking rice plays a crucial role in determining its glycemic index, which affects its impact on blood sugar levels. Here are some cooking techniques that can help you lower the glycemic index of your rice:
- Cook rice slowly using a pan: Instead of using a pressure cooker or rice cooker, opt for traditional stovetop cooking in a pan. This slower cooking process can help reduce the glycemic response of rice.
- Add more water: Increasing the water-to-rice ratio can further lower the glycemic index. Aim to add approximately 1.5 to 2 cups of water for every cup of rice.
- Include fiber-rich foods: To slow down the digestion process and minimize blood sugar spikes, incorporate fiber-rich ingredients when cooking rice. Lentils, legumes, leafy vegetables, and spices are excellent choices to enhance the nutritional value and fiber content of your meal.
Portion control is essential when incorporating rice into a diabetic meal plan. The amount of rice consumed should be based on factors like age, physical activity level, and diabetes control goals. By practicing portion control and utilizing these cooking techniques, you can enjoy low-Gi rice while effectively managing blood sugar levels.

Other Low-Gi Alternatives to White Rice
Apart from the low-Gi rice options mentioned earlier, there are several other alternatives to white rice that diabetics can incorporate into their meal plans. These alternatives provide variety and additional nutritional benefits for those looking to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Bulgur
Bulgur is a nutritional powerhouse with a GI of 46. It is a whole grain that is rich in fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals. Bulgur is commonly used in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean cuisines, and it adds a chewy texture and nutty flavor to dishes.
Quinoa
Quinoa is a complete protein source, making it an excellent choice for vegetarians and vegans. It has a GI of 53 and is packed with essential amino acids, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Quinoa is versatile and can be used as a base for salads, stir-fries, and even as a substitute for rice in pilafs and side dishes.
Freekeh
Freekeh is a prebiotic cereal with a GI of 43. It is made from young, green wheat that is roasted and cracked. Freekeh is high in fiber, protein, and antioxidants. It has a unique smoky flavor and a chewy texture, making it a great addition to soups, stews, and grain bowls.
Cauliflower Rice
Cauliflower rice is a low-carb and low-GI alternative to white rice, with a GI of 0-15. It is made by pulsing cauliflower florets in a food processor until they resemble rice grains. Cauliflower rice is a great option for those following a ketogenic or low-carb diet. It can be used in a variety of dishes, including stir-fries, fried rice, and grain-free sushi rolls.
Shirataki Rice
Shirataki rice is made from the konjac yam and has a GI of 0. It is extremely low in calories and carbohydrates, making it a suitable option for those looking to control their blood sugar levels and manage their weight. Shirataki rice has a gelatinous texture and is commonly used in Asian cuisine.
By incorporating these low-Gi alternatives to white rice, individuals with diabetes can enjoy a wider range of flavors and textures while still maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
When it comes to managing blood sugar levels, finding the right rice options for diabetics is crucial. By choosing low-Gi rice varieties, like brown rice and whole grain basmati rice, individuals with diabetes can enjoy the nutritional benefits of rice while keeping their blood sugar in check. These healthy rice choices provide essential nutrients and fiber that can aid in regulating blood sugar levels.
In addition to low-Gi rice options, incorporating other fiber-rich foods into the meal plan is essential. This includes lentils, legumes, and leafy vegetables, which can further slow down the digestion process and minimize the impact on blood sugar levels. Portion control is another important consideration to ensure a balanced diabetic diet.
With the right choices and cooking techniques, rice can be a delicious and nutritious addition to a diabetic meal plan. It is important to prioritize low-Gi rice options and manage portion sizes to effectively manage blood sugar levels. By incorporating these strategies, individuals with diabetes can enjoy a variety of healthy rice choices that support their overall well-being.
Source Links
Types of Rice and their Glycemic Index (GI)
Black rice (aka forbidden rice)
Type:Long-grain rice, a variant of brown rice
Black rice was also known as the forbidden rice in ancient Chinaas it was only for the royalsdue to its rich nutritional content and medicinal properties. Its deepcolourcomes from anthocyanins, an antioxidant found in dark purple or red fruits and vegetables. They are high in zinc, iron,fibreand vitamins such as B6 that provides the body with a variety of benefits.
After cooking, it turns into a deep purple shade,holdinganuttycaramelflavour, with a slight crunch in texture. This rice can be consumed on its own to go along with dishes. Its other common use is in local desserts like pulut hitam.
GI level: Low
The choice of rice we consumedaily,and its GI level affects our bodies in the long run as eating foods high in GI can cause rapid spikes inbloodglucoselevelin our bodies.In time, if blood glucose levels are sustainably high, there is a higher risk of of developing Type 2 diabetes, heart diseases and various other health problems. It is beneficial to seek lower GI food alternatives to maintain a healthier bloodglucoseleveland prevent risks of health problems.
Which Rice has the Lowest Glycemic Index?
Which Rice has the Lowest Glycemic Index?
Rice is a standard part ofour daily diet. They can be high in carbs. Yet, some types of rice like the brown rice, and known to be whole-grain foods. Whether it is lunch or dinner, rice is consumed frequently in every house meals. The health benefits that come with rice and the soft juicy taste of rice make them a favorite food for almost everyone. Read more about Which Rice has the Lowest Glycemic Index?.
In many Asian countries, rice is an essential part of the daily meal. Yet, all the countries and cities around the world have introduced various tasty and unique rice recipes. Altogether, we can say that rice is a widely consumed food around the world.
This huge demand for rice has also introduced plenty of varieties n this food. Today, rice is available in different types, including Indica rice, Calrose rice, japonica rice, etc. Other than these multiple varieties, there are plenty of rice products also available in the market. All the different rice products have different GI values. For diabetic patients and dieters, consuming low-GI rice is very important. For this, it is essential to understand how the GI value of rice may be affected. Lets discover more about the low-GI rice below.
Which Rice has the Lowest Glycemic Index?Types of Rice with Different GI-Values:
Rice is not eaten plain. Instead, rice is consumed with other food items in almost every country/region. So it is essential to understand what rice (or rice products) has low or medium GI values for combination meals. You can understand the GI values of rice if:
- The rice varieties are longer grain. Such rice usually has high amylose content (approx. 19-23%). As a result, such rice has a low-GI value
- The rice varieties are of a shorter grain. These varieties have lower amylose content (approx. 12-19%). So they can have various GI values. This value can be as low as 43 or increase to as high as 96.
Other Factors Affecting the GI-Value of Rice:
Other than the type of rice grain you choose, there are plenty of other factors that may affect the rice GI value. This can include the various types/cooking methods of rice. For instance:
- According to studies, brown rice or parboiled white rice has a medium-GI value. Their GI value can range from 56 69. So you can combine such rice with other foods to have a meal with a balanced GI.
- The cooking method also affects the GI value of rice. There are many cooking methods used to make rice, including boiling, steaming, frying, etc. Some cooking methods may increase rices GI value, while others may decrease or balance the value. It is essential to understand how you cook your rice before consuming them with other foods. A great way to consume low-GI rice meal is to consume cooled rice with legumes.
Note:you can also consume substitutes of white rice to decrease the GI value of your meal. Some great grain substitutes of white rice include white rice, quinoa, and pearl barley.
Bottom Line Which Rice has the Lowest Glycemic Index?:
In the end, if you want to consume thelowest glycemic indexrice, then you can look for the long grain varieties.Studies showthese rice varieties have a lower-GI value, so they are suitable for mass consumption in combination meals. But the types of rice and its cooking style also affects the GI value of rice.
So it is essential to ensure that you are cooking low-GI rice in the right way. For thelowest glycemic indexof rice, you can boil and then refrigerate rice before consuming them. In this way, you can maintain your blood sugar levels. So this concludes the topic for Which Rice has the Lowest Glycemic Index?. White vs Brown Rice