What is the lowest GI bread

Glycemic Index
Low GI Bread
With the increasing popularity of GI diet, low GI breads also started to appear on supermarket shelves.
Low-GI bread helps youkeep full longer, avoid cravings and help stabilize yourblood sugar levelsby a slow release of energy.
Addingsoy flour, seeds, nutsandwhole grainsto bread helps make it high in fiber and low in GI. Interestingly, addingvinegaralso does lower its GI value.Insoluble dietary fiberfound in these breads helps lower blood cholesterol, stimulate bowel function and prevent constipation.
Please be aware that very few of the breads in the market are actually in the low GI range- equal to or below 55 and most do havemedium GI valuesof between 56 and 69.
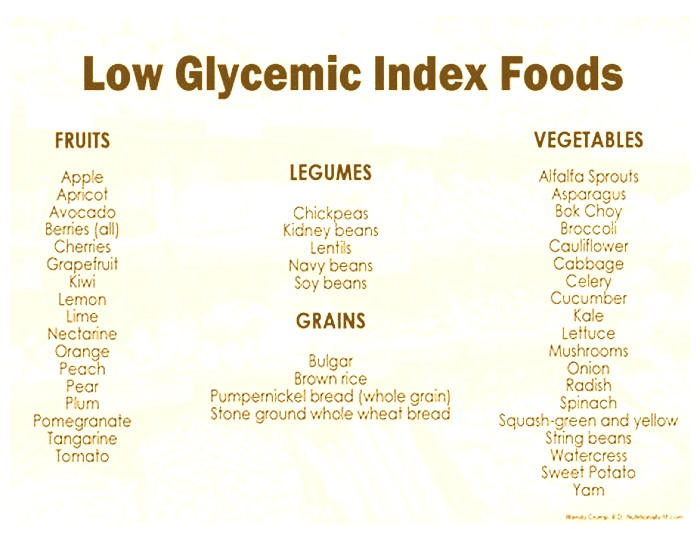
Whole grainsinclude rye, barley, oats, seeds and cracked wheats and they are high in fiber, minerals and vitamins, low in GI depending on how much grains they have.
Your best option is to check for theGI symbolon breads, bread being labeled as wholemeal, whole grain or sourdough will not always mean they are low in GI. Sure they will be much healthier than white breads, there is no doubt.
It was a bit of a surprise when I first found outwhite breadcaused as much or even bigger spike and crash than glucose in blood sugar. Yes it has a GI value of up to 100 depending on how processed and fresh it is.
The morefluffierand the lessdensea bread or a bread product is, the higher its GI value with a negative effect on blood sugar levels.
High GI bread, particularly plain and fluffy white bread is believed to be responsible for variousdigestive problemsas well as for complications leading todiabetes.
However, low GI bread probably isnt your best option if you need to eat wheat, soy or gluten free due toallergies. These breads are baked with various wheat products to be able to increase the fiber content.

Types of Low GI Breads:
Sourdough breadmay be low or high in GI depending on how much sourdough is added to white bread. If you like the taste of white bread, sourdough is the closest you will get to it as a type of low GI bread.
Soy and linseed breadis higher in fat than other breads but the fat content is unsaturated and this bread is a good source of Omega-3 fatty acids and dietary fiber as well being a great low GI bread.
Same goes forwhole grain bread it are generally known to be low in GI but how much fiber, grains or amylose starch there are in the bread as well as how processed the bread is, will influence the glycemic index value.
In case ofwhole mealor brown bread, enzymes are used to soften the crust making it easily digestible, hence making it higher in GI.
Stone-ground breadis also low in GI as the stone-ground flour is coarser and digested much slower.
Fruit loafis fine in terms of GI value, as long as it is dense and contains plenty of nuts, seeds and dried fruits.Return from Low GI Bread to Glycemic Index home pageOr take me back to Complex Carbohydrates page

Whats the best bread for people with diabetes?
Bread is a popular food and a key element of diets in many countries. However, it is often high in carbohydrates, so people with diabetes may wonder if they can still eat it.
The good news is that bread can form part of a healthy diabetes eating plan. It is one of many carbohydrate-containing foods a person can choose to include within their carbohydrate budget for each meal or snack.
This article will explore how people with diabetes can include bread in their diet and list some of the healthier choices available.
There are two main types of diabetes, type 1 and type 2. People manage them with lifestyle changes and medication.
Diabetes development
Type 1 diabetes happens when the body cannot produce insulin, a hormone that captures blood sugar, also called glucose, and transfers it into cells. Glucose is the preferred energy source for cells.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form. According to the
The
Prediabetes means a person has high blood sugar levels, but not as high as those with diabetes. Prediabetes can potentially develop into diabetes. However, managing blood sugar can help prevent or delay this.
Blood sugar management
With prediabetes or diabetes, a person can improve their health and lower the risk of complications by taking steps to manage the condition. Nutrition plays
Carbohydrates are one of the three major nutrients essential to human health. However, the body converts carbohydrates into glucose, which it absorbs into the bloodstream, raising blood sugar. For this reason, being aware of carbohydrate intake is part of managing blood sugar levels with diabetes or prediabetes.
The American Diabetes Associations Diabetes Plate Method is a tool to help plan diabetes-friendly meals. According to this method, the makeup of a persons plate should consist of the following:
- one-half nonstarchy vegetables such as carrots, leafy greens, broccoli, and peppers
- one-quarter lean proteins such as lean meats, fish, or tofu
- one-quarter carbohydrates
Carbohydrate foods suitable for a diabetes eating plan include:
- starchy vegetables, such as peas, potatoes, and squash
- beans and legumes, such as chickpeas, black beans, and kidney beans
- fruits
- dairy products, such as yogurt and milk, or nondairy milk substitutes
- whole grain products such as bread, brown rice, and oats
Everyones body responds differently to food, including carbohydrates. A person can consult a doctor or registered dietitian to develop a personalized diabetes eating plan to help manage blood sugar according to their individual needs.
Managing portions
Bread is one of many grain products a person can choose to eat within the carbohydrates category.
However, managing portions is important to ensure they only make up one-quarter of the whole plate when following the Diabetes Plate Method.
Eating more bread than the recommended amount may make it harder to meet overall goals for carbohydrate intake and manage blood sugar levels.
Checking sugar content
When producers use yeast to make bread rise, the bread usually needs some sugar to feed the yeast.
Some commercial bread types contain more sugar than is necessary to make it rise. A person can check the nutrition label to see the number of carbs and added sugars in a slice of bread.
Most commercial white bread contains only
Serving bread
People can further reduce the carb content of a meal containing bread by choosing spreads carefully, for example, serving it with unsweetened peanut butter or avocado instead of jellies or chocolate spread.
Types of bread that may be healthier options for people managing diabetes include:
100% whole grain
Most commercially-available bread options contain refined white flour. This provides little to no fiber. Even wheat bread may contain refined wheat, not whole grain wheat flour.
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate the body cannot digest. It keeps the bowels regular and helps promote a feeling of fullness.
Fiber can also help control blood sugar. According to a
Whole grain bread naturally contains fiber. However, some brands that identify their bread as seven-grain or nine-grain only use those grains on the crust, while most of the bread still consists of refined white flour.
A person can read the ingredients list to check for 100% whole grain or whole wheat flour as the first ingredient in commercial bread. This will contain more nutrients.
Fiber-enriched
Bread can be a good source of fiber if it contains 3 or more grams per slice. Some breads are available that have extra soluble fiber added.
However, fiber-enriched whole grain breads are still relatively high in carbohydrates, so it is important to eat them in moderation.
Low carbohydrate tortillas
Tortillas can provide a tasty, versatile, and sometimes healthier choice for sandwiches. Manufacturers are increasingly providing a wider range of low carbohydrate tortillas.
Many of these have added fiber to reduce the carbohydrate count. Some tortillas contain low carbohydrate ingredients, such as whey and soy protein powders.
People can use low carbohydrate tortillas as they would bread, wrapping their favorite sandwich ingredients in the tortilla. They can also use them for mini pizzas, homemade burritos, and tacos.
Bread recipes
Many recipes for making grain-free bread are available online.
However, these breads tend to be more expensive to make and often yield a smaller amount compared with traditional bread recipes. Depending on the ingredients, the carbohydrate, sugar, and fiber contents may not provide any benefits over traditional whole grain bread.
If a person chooses to bake their own bread, they might consider a 100% whole wheat, low sugar recipe.
However, knowing the exact carbohydrate content of homemade bread can be challenging, so it may not be suitable for all eating plans.
Checking ingredient lists and nutrition labels on bread packaging can help people with diabetes choose a suitable product.
To recap, to help manage blood sugar, it is most important to choose bread that is:
- 100% whole grain, such as 100% whole wheat
- a good source of dietary fiber, containing at least 3 grams per slice
- low in added sugars, with only 13 grams per slice
Some specialty ingredients may provide additional fiber, protein, and healthy fats. These include:
However, bread containing these ingredients can be expensive. Portion-for-portion, they are unlikely to offer extra benefits for managing blood sugar. A budget-friendly 100% whole wheat bread is an equally good choice for a diabetes eating plan.
People with diabetes can choose to include bread and bread products in their diet. However, in a diabetes eating plan, people will need to manage bread portions so as not to exceed their total carbohydrate budget.
Whole grain, high fiber breads with minimal added sugar may be the best options.
Continuing an exercise program, using doctor-prescribed medications, and following a diabetes eating plan are the most effective ways for people with diabetes to manage their blood sugar while continuing to eat the foods they enjoy.
Glycemic Index of Bread
Glycemic Index of Bread
The glycemic index of bread depends on the types of grains and refined sugars used during the baking process.
Care should be taken to select breads with a low GI value, which includes a number of popular sourdough and rye breads.Certain types of bread, particularly those with larger, coarser grains, our sourdough breads whose acidity counteracts the rapid release of glucose, are excellent choices.
Take care when choosing regular grocery store breads however. Most of these are heavily refined and enriched. Look for coarse grains, seeds, and heavier blends!
The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels. Generally, bread made from refined white flour has a higher GI compared to bread made from whole grains. Here are some common types of bread and their GI scores:
- White bread high GI score (70 or above)
- Whole wheat bread medium GI score (56-69)
- Sourdough bread lower GI score (50-69)
- Rye bread lower GI score (40-59)
- Pumpernickel bread lower GI score (41-46)
Its important to note that the GI score is just one factor to consider when making food choices, and that other factors such as the amount and type of carbohydrate, fiber content, and overall nutritional value should also be taken into account.
Glycemic Index of Wheat Bread, White Bread, Sourdough | Type of Bread | Glycemic Index Score |
 | Dark Rye | 51 |
 | French Baguette | 95 |
 | Hamburger Bun | 61 |
 | Kaiser Roll | 73 |
 | Pita Bread Whole Wheat | 57 |
 | Sourdough | 52 |
 | Fruit Bread | 53 |
 | White Bread | 70 |
 | Wonder Bread, White | 71 |
 | Wheat Stoneground Bread | 53 |
 | Whole Wheat | 69 |
 | Bagel, plain, white | 72 |
 | Wholegrain Bread | 40 |
 | Multigrain Breads | 45 |
 | English Muffin, Whole Grain | 45 |
 | Oat Bread | 65 |
 | Rye Bread | 50 |
 | Bran Muffin | 65 |