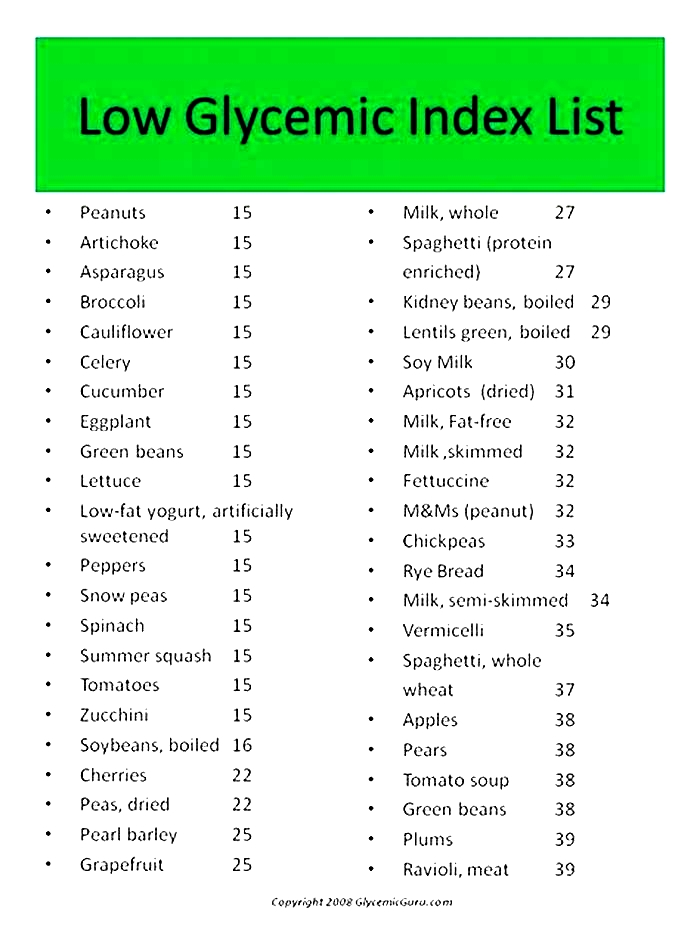
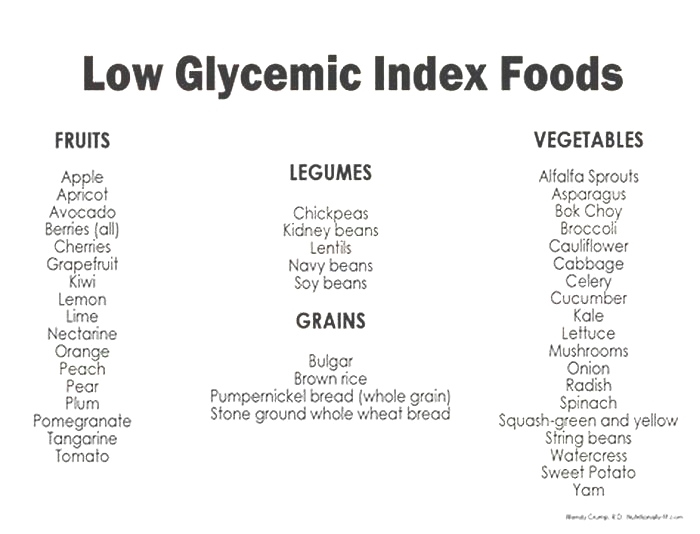
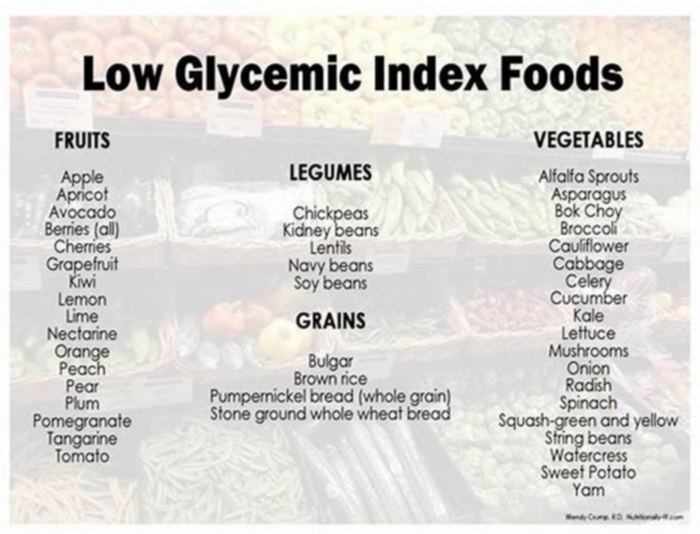
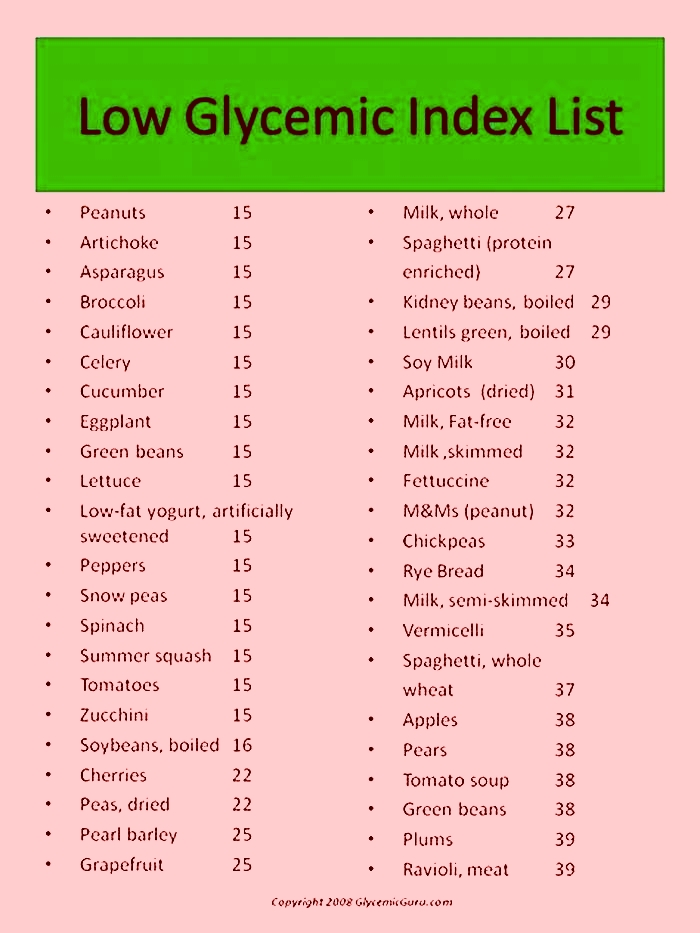
What foods are low glycemic index for dogs
When and how you feed is crucial to caninehealth
If your dog is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, your veterinarian will help you with insulin dosages. Its not all about insulinthough. Blood glucose levels affectwhat your dog eats, as well as how much they eat too.
Diabetes relates to excess blood glucose (or sugar). Your dog needs just the right amount of glucose in theirbloodstream. Too much, and they will drink and pee far more than usual. Too little, and theywill collapse from hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). In this article, weve outlined some things to keep in mind when feeding a diabetic dog.
Timing
A diabetic dog needs correctly timed meals, instead offree will feeding. Meals 10-12 hours apart work best for most dogs.
Insulin injection
If you can give your dog a treatafter receiving an insulin injection, it provides a more positive association with the injection.
Remember: If your dog skips a meal, do notgive them an insulin dose because it could triggerhypoglycemia. Call your veterinarian if your dog is not eating.
Palatability
Your diabetic dog must eat regularly. If theydont eat, theydont getmedicine. So, you must find a food your dogconsistently consumes. Be careful with treats. If you need treats for training, discuss your choices with your veterinarian. Excessive treats or treats with a lot of carbohydrates, which affect blood sugar, could throw offinsulin regulation.
Avoid highly digestible diets
Highly digestible diets are often yummy, but they are high in sugars. These foods often lead toglucose spikes right after eating and corresponding big drops in blood sugar soon thereafter.
Go prescription
Prescription diets, available through your veterinarian, use ingredients to evenout blood glucose levels, making it easier to keep your dog ona steady dose of insulin. They also must limit fat intake to prevent complications, such as pancreatitis.
Fiber choices
Much of the fiber in your diabetic dogs diet should be insoluble, as this will help your dogfeel full but not provideexcesscalories. Insoluble fiber promotes the movement of food through the digestive tract. Soluble fiber attracts water, turns to geland slows digestion, resulting in more calories released in the colon. For diabetic dogs, moving the food through the digestive tract quickly is advantageous.
For an overweight dog, a diet with 10-20% of the dry foodas fiber is a good plan. For a dog who is in good weight or slightly underweight, look for a diet with 5-15% fiber on a dry basis.
Most guaranteed analyses will not tell you if the fiber in the diet is insoluble or soluble. You will need to look at the ingredient list andconsult with your veterinarian or a veterinary nutritionist. Beet pulp, guar gumand psyllium are common sources of soluble fiber. Cellulose is an example of insoluble fiber.
Weigh-ins
Many diabetic dogs are overweight. If your diet plan includes some weight loss, do frequent weigh-ins at your veterinary clinic so that your dogs insulin dosage can be adjusted as needed. Underweight dogs will need different dietary considerations than overweight dogs. Track your dogs weight as well as glucose levels.
Low fat
Low fat is important for diabetic dogs, since as many as 30% of them become diabetic secondary to pancreatitis. Of course, this is more criticalfor overweight diabetic dogs.
Supplementing with L-carnitine may help with fat metabolism for these dogs. L-carnitine is a natural derivative from the amino acid lysine, and itis often included in weight-loss supplements. Look for a dry-matter carbohydrate level of 25%. Read the ingredientlist for carbohydrates that havea low glycemic index, like soybeans. In contrast, potatoes have a high glycemic index.
Knowing yourdog's specific needs
Finally, if your dog is a well-managed diabetic, do not change theirdiet. Even changing protein sources like switching from a chicken-based recipe to a lamb-based one can influence blood glucose levels.
Changes in your dogs diet may require correspondingchanges in insulin. The ideal diet and feeding regimen for your diabetic dog is the one that keeps their glucose at a steady level.
This article has been reprinted with permission from the Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicines DogWatch newsletter, published by Belvoir Media Group. When you become a member of the Riney Canine Health Center, you will receive a free subscription to DogWatch.
A guide to diabetic dog food
Diabetes is a chronic illness that affects dogs just as much as humans. The most common kind of diabetes in dogs is diabetes mellitus, a condition that affects their ability to transport the glucose, or sugar, in their bloodstream to other parts of their body. Glucose, produced when the body breaks down the nutrients in food, fuels the bodys organs and cells. A hormone known as insulin is in charge of delivering that fuel from the bloodstream to the cells.
Canine diabetes is a rising health issue affecting as many as 1 in 300 dogs, an 80% jump since 2006. While diabetes isnt curable, it is manageable with the appropriate steps. This starts with understanding the nutrition, exercise, and medical care diabetic dogs need to lead healthy lives.
A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids can help prevent conditions that lead to diabetes in the first place.
Some omega-3 products are extracted oil supplements, but ZipZyme Omega is a fresh food sustainably grown from ocean algae. In addition to the traditional benefits of omega-3s, ZipZyme preserves the algaes special enzymes that multiply the amount of DHA and stop the accumulation of unhealthy saturated fats in the body. Docosahexaenoic acid or DHA is the most important omega-3 fatty acid.
Best Dog Food For Diabetes
DogFoodAdvisor is reader supported See how
All reviews are 100% impartial but if you buy using links on this page, we may earn a referral fee.
Whats the best dog food for diabetes?
Diabetes is a relatively common disorder in dogs, with around one in 200 affected.
When it comes to managingdiabetes in dogs, its important to provide them with a well-balanced diet that helps regulate their blood sugar levels.
You should choose a food which contains lean sources of protein such asskinless chicken,turkey,lean beeforfish. Proteins are essential for maintaining muscle mass and overall health.
Food which includes non-starchy vegetables such asbroccoli,cauliflower,green beans,Brussels sprouts, andspinachare also important. These vegetables have a low glycemic index, which means they have minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
Fiber-rich foods can help slow down the absorption of glucose, promoting better blood sugar control. Opt for sources such aspumpkin,sweet potatoes,carrots, andgreen leafy vegetables.
If you include grains in your dogs diet, choose wholegrains likebrown riceorquinoaas these contain more fiber and have a lower glycemic index compared to refined grains.
Sources of healthy fats such asfish oilorflaxseed oil, can be beneficial for dogs with diabetes as they help promote a healthy coat and skin.
See our list of thebest dog foods for diabetes, but please remember it is important to work closely with your veterinarian to develop a specific meal plan for your diabetic dog. They can provide guidance on portion sizes and specific dietary requirements based on your dogs individual needs.
Additionally, monitoring your dogs blood glucose levels regularly and adjusting their diet accordingly is crucial for managing diabetes effectively.
Chicken is one of4 recipesincluded inour reviewof the The Farmers Dog fresh product line.
The Farmers Dog Chicken Recipe derives the bulk of its meat protein fromchicken. Dry matter label analysis reveals the recipe contains 46% protein, 34% fat and 12% estimated carbs resulting in a fat-to-protein ratio of about 74%.
Read our review of the full The Farmers Dog Food (Fresh) range here
Main Ingredients Chicken, brussels sprouts, chicken liver, bokchoy cabbage, broccoli Type Grain-Free Protein Percentage 46% AAFCO Standards All Life Stages Best For Puppies and dogs Turkey & Pumpkin Pate is one of11 recipesincluded inour reviewof the Raised Right Fresh product line
Raised Right Turkey & Pumpkin Pate derives the bulk of its meat protein fromturkey. Dry matter label analysis reveals the recipe contains 60.7% protein, 21.4% fat and 9.9% estimated carbs resulting in a fat-to-protein ratio of about 35%.
Read our review of the full Raised Right Dog Food (Fresh) range here
Main Ingredients Turkey thigh, pumpkin, turkey heart, turkey liver, organic spearmint. Type Grain-Free Protein Percentage 60.7% AAFCO Standards Maintenance Best For Dogs Sample buyer review...
Read more buyer reviews at RaisedRightPets.com"I have 2 rescues. Since I have been giving them Raised Right, they are ow at a healthy weight & the intermittent GI problems that they were experiencing have completely disappeared. As stated, best dog food ever"
Turkey & Chicken is one of12 recipesincluded inour reviewof the Wellness CORE product line.
Wellness CORE Grain-Free Reduced Fat (Turkey & Chicken) derives the bulk of its meat protein fromturkey. Dry matter label analysis reveals the recipe contains 36.7% protein, 11.1% fat and 44.2% estimated carbs resulting in a fat-to-protein ratio of about 30%.
Read our review of the full Wellness Core Dog Food (Dry) range here
Main Ingredients Deboned turkey, turkey meal (source of glucosamine), chicken meal (source of chondroitin sulfate), peas, dried ground potatoes. Type Grain-Free Protein Percentage 36.7% AAFCO Standards Maintenance Best For Dogs Sample buyer review...
Read more buyer reviews at WellnessPetFood.com"My collie was diagnosed with diabetes four years ago after a rough 6-12 months trying to get her regulated and trying several different brands of food we tried wellness reduced fat and havent looked back we managed to regulate her shortly after and shes been doing great on it we also switched our malamute to it as well and he also had dietary issues with a sensitive stomach and would turn his nose upto different brands they both eat this without fail and both have great coats and health out groomer even commented on our malamutes poo how healthy it was! Sorry TMI!!! Mysti pictured is now 13.5 years and still doing well her sight did go shortly after diagnosis but she has full vision and nice bright eyes again!"
Taste of the Wild Southwest Canyon with Wild Boar is one of9 recipesincluded inour reviewof the Taste of the Wild product line.
Taste of the Wild Southwest Canyon with Wild Boar derives the bulk of its meat protein frombeef. Dry matter label analysis reveals the recipe contains 32.2% protein, 16.7% fat and 43.1% estimated carbs resulting in a fat-to-protein ratio of about 52%.
Read our review of the full Taste of the Wild Dog Food range here
Main Ingredients Beef, peas, garbanzo beans, lamb meal, canola oil. Type Grain-Free Protein Percentage 32.2% AAFCO Standards Growth & maintenance Best For Puppies & Dogs Sample buyer review...
Read more buyer reviews at TasteOfTheWildPetFood.com"Our dogs love TOTW and we do too! Although our dogs have their favorite flavors they seem to like all the ones we have tried. They get excited when we bring the bag in! We as owners take great comfort in knowing that TOTW has our dogs health in mind when making their product."
Real Salmon & Sweet Potato is one of12 recipesincluded inour reviewof the Merrick Grain-Free Dry product line.
Merrick Grain-Free Dry Real Salmon & Sweet Potato recipe drives the bulk of its protein fromsalmon. Dry matter label analysis reveals the recipe contains 38.2% protein, 15.7% fat and 38.1% estimated carbs resulting in a fat-to-protein ratio of about 41%.
Read our review of the full Merrick Dog Food range here
Main Ingredients Deboned Salmon, salmon meal, whitefish meal, sweet potatoes, potatoes. Type Grain-Free Protein Percentage 38.2% AAFCO Standards Maintenance Best For Dogs Sample buyer review...
Read more buyer reviews at MerrickPetCare.com"Merrick Grain Free Dog Food is worth it for the pup in our family!! We know we are feeding our dog food with great ingredients, taste, and quality. Our dog maintains a healthy weight, active energy, and positive spirit while eating Merrick Dog Food. While she loves many of the varieties, her favorite flavor is Salmon and Sweet Potato."
Farmina Ancestral Grain Adult Mini Dry Chicken & Pomegranate is one of13 recipesincluded inour reviewof the Farmina Ancestral Grain product line.
Farmina Ancestral Grain Adult Mini Chicken & Pomegranate derives the bulk of its meat protein fromchicken. Dry matter label analysis reveals the recipe contains 33% protein, 19.8% fat and 39.3% estimated carbs resulting in a fat-to-protein ratio of about 60%.
Read our review of the full Farmina Ancestral Grain Dog Food (Dry) range here
Main Ingredients Boneless chicken, dehydrated chicken, whole spelt, whole oats, herring Type Grain Protein Percentage 33% AAFCO Standards All Life Stages Best For Puppies and Dogs Sample buyer review...
Read more buyer reviews at Farmina.com"This is the nutritionally best food you could ever feed your pup. Huge diff in my poodles coat and overall health. Well worth the extra money if your needing to feed a dry kibble but want to retain some type of raw food diet value. Highly recommended"
The Real Chicken & Vegetable Dry is one of6 recipesincluded inour reviewof the Racheal Ray Nutrish product line.
Rachael Ray Nutrish Real Chicken & Vegetable drives the bulk of its meat protein fromchicken. Dry matter label analysis reveals the recipe contains 29.5% protein, 15.9% fat and 46.5% estimated carbs resulting in a fat-to-protein ratio of about 54%.
Read our review of the full Rachael Ray Dog Food range here
Main Ingredients Chicken, chicken meal, soybean meal, grain sorghum, dried peas Type Grain Protein Percentage 29.5% AAFCO Standards All Life Stages Best For Puppies and Dogs Sample buyer review...
Read more buyer reviews at Nutrish.com"Ive been feeding Rachael Ray dog food to both my lab and my English bulldog the last 10 years. Ive tried different dog foods but this is my first choice. this seems to be easy on their stomach and helps me with controlling their weight"
More Top Picks
To view more top dog foods by category click the link below that best meets your personal feeding needs.
Here are the most frequently asked questions we get about diabetes:
Frequently Asked Questions
How is diabetes diagnosed in dogs?
Diagnosing diabetes in dogs typically involves a combination of clinical assessment, physical examination, and specific diagnostic tests.
The veterinarian will inquire about your dogs overall health, any noticeable symptoms, changes in behavior, and any predisposing factors that could increase the risk of diabetes.
They will then carry out a thorough physical examination, checking for signs such as weight loss, dehydration, changes in coat condition, and overall body condition.
Blood and urine tests are crucial in diagnosing diabetes in dogs. The vet will typically perform the following tests:
- Blood glucose level: A high blood glucose level (hyperglycemia) is a significant indication of diabetes. In some cases, a glucose curve may be conducted to evaluate glucose levels over time
- Glycosuria: The presence of glucose in the urine indicates that the kidneys are excreting excess glucose, suggesting diabetes.Fructosamine test: This blood test measures average blood glucose levels over the past two to three weeks, providing a broader perspective of glucose control
What are the symptoms of diabetes in dogs?
The main symptoms to look out for are:
- Increased thirst (polydipsia): Dogs may start drinking larger amounts of water than usual
- Frequent urination (polyuria): Dogs may need to urinate more frequently or have accidents indoors
- Increased appetite (polyphagia): Despite eating more, dogs may experience weight loss or have difficulty maintaining weight
- Weight loss: Dogs may lose weight even though their appetite has increased
- Lethargy: Dogs may appear tired, lacking energy, or less active than usual
- Urinary tract infections: Dogs with diabetes are more prone to developing urinary tract infections
- Sweet-smelling breath: Some owners may notice a fruity or sweet odor on their dogs breath
- Vision problems: In advanced cases of diabetes, dogs may develop cataracts, resulting in cloudy eyes or vision impairment
- Dehydration: Due to increased urination and water intake, dogs with diabetes may become dehydrated
- Poor coat condition: The dogs coat may become dull, dry, or develop hair loss
What causes diabetes in dogs?
Certain dog breeds are more prone to developing diabetes than others, including poodles, beagles, dachshunds, samoyeds, cairn terriers, and miniature schnauzers.
In some cases, diabetes in dogs is considered an autoimmune disease, where the bodys immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This leads to an insufficient production of insulin.
Obesity is also a significant risk factor for diabetes in dogs. Excess body weight can lead to insulin resistance, meaning the bodys cells become less responsive to insulin. As a result, the pancreas produces more insulin to compensate, eventually leading to the pancreas being unable to keep up with the demand.
Inflammation of the pancreas, known as pancreatitis, can disrupt the normal insulin production and secretion. Repeated or severe cases of pancreatitis may increase the risk of developing diabetes.
Certain hormonal conditions, such as Cushings disease (hyperadrenocorticism) or an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism), can affect insulin regulation in the body too and potentially lead to diabetes.
What dietary changes should be made for a diabetic dog?
Dietary changes are an essential aspect of managing diabetes in dogs. The primary goals of the diet for a diabetic dog are to regulate blood glucose levels, maintain a healthy weight, and provide balanced nutrition.
Here are some key considerations:
Feeding your diabetic dog consistent meals at regular intervals is important to help stabilize blood sugar levels. Divide the daily food portion into two or more equally sized meals, given at the same time each day.
Choose a high-quality commercial dog food that is specifically formulated for diabetic dogs or recommended by your veterinarian. Look for diets that are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, as they can help regulate blood glucose levels. Avoid foods with excessive amounts of sugars, simple carbohydrates, and high-fat content.
Work with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate portion sizes for your diabetic dog. Portion control is crucial to manage weight and blood glucose levels effectively.
Select foods with a low glycemic index (GI). These foods release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Foods such as whole grains, legumes, and certain vegetables have a lower GI and can be beneficial for diabetic dogs.
Ensure that the diet provides a balanced ratio of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. High-quality proteins help maintain muscle mass, while complex carbohydrates and moderate amounts of healthy fats contribute to overall nutrition.
Limit or eliminate high-sugar treats and snacks from your dogs diet. Instead, opt for diabetic-friendly treats or use low-sugar alternatives such as small pieces of cooked lean meat or vegetables.
Establish a routine feeding schedule and avoid free-feeding (leaving food out all the time). This helps with insulin management and monitoring your dogs appetite.
Can I still give my diabetic dog insulin injections at home?
Yes, in most cases, you can administer insulin injections to your diabetic dog at home. Many dog owners successfully manage their dogs diabetes by administering insulin injections themselves. However, it is important to work closely with your veterinarian to learn the proper technique and ensure you are using the correct type and dosage of insulin for your dogs specific needs.
Here are some important points to consider:
Your veterinarian will determine the appropriate type of insulin for your dog, the dosage, and the frequency of administration. They will also teach you how to properly handle and administer the insulin. It is essential to follow their instructions closely.
Insulin injections are typically given under the skin. Your veterinarian will show you the correct technique, which involves pinching a fold of skin and inserting the needle into that fold. They may recommend specific injection sites and rotation to prevent tissue irritation.
Regular monitoring of your dogs blood glucose levels is crucial to assess the effectiveness of insulin therapy and adjust the dosage if needed. Your veterinarian may teach you how to perform at-home blood glucose monitoring or recommend periodic visits for testing.
Insulin should be stored as instructed by your veterinarian, usually in the refrigerator. Follow proper handling procedures and expiration dates to ensure the insulins efficacy and safety.
It is important to prioritize safety while administering insulin injections. Take measures to ensure a calm and controlled environment during the process. Avoid distractions that may startle or stress your dog.
Keep your veterinarian informed about your dogs progress, any changes in symptoms, and the response to insulin therapy. Regular communication allows your veterinarian to make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
It is worth noting that in some cases, if a dogs diabetes management becomes complex or their condition is unstable, veterinary hospitalization or assistance from a professional veterinary nurse may be required.
Always consult with your veterinarian for personalized advice and guidance specific to your dogs condition. They can provide detailed instructions and support to help you safely administer insulin injections at home.
How frequently should I monitor my dogs blood sugar levels?
The frequency of monitoring your dogs blood sugar levels can vary depending on several factors, including the stability of their diabetes, the type of insulin used, the response to treatment, and any changes in their overall health condition.
What are the potential complications or risks associated with diabetes in dogs?
If not properly managed, diabetes in dogs can lead to various complications including:
- Hypoglycemia: This occurs when blood sugar levels drop too low. It can happen if too much insulin is administered, if the dog doesnt eat properly, or if there is excessive exercise. Hypoglycemia can be dangerous and may cause weakness, disorientation, seizures, or even coma if not promptly treated.
- Hyperglycemia: This refers to high blood sugar levels, which can occur if the dogs diabetes is not well-regulated. Prolonged hyperglycemia can lead to dehydration, weight loss, increased susceptibility to infections, and other complications
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): This is a severe complication that can occur when a diabetic dogs body breaks down fats for energy instead of glucose. This process produces ketones, which can build up in the bloodstream, leading to metabolic acidosis. DKA is a life-threatening condition and requires immediate veterinary attention. Symptoms may include lethargy, loss of appetite, vomiting, dehydration, and a distinctive fruity odor on the breath.
- Cataracts: Uncontrolled diabetes in dogs can lead to the development of cataracts. Cataracts cause clouding of the lenses of the eyes, leading to impaired vision or blindness if left untreated
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Dogs with diabetes are more susceptible to developing urinary tract infections. High levels of glucose in the urine provide a favorable environment for bacterial growth, leading to recurrent infections
- Pancreatitis: Dogs with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing pancreatitis, which is inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis can further disrupt insulin production and regulation, exacerbating diabetes control
- Organ damage: Prolonged uncontrolled diabetes can affect various organs, including the kidneys, liver, heart, and blood vessels. Over time, these complications can impact the overall health and quality of life of the dog
Its important to note that with proper management, including insulin therapy, appropriate diet, regular exercise, and close veterinary monitoring, the risk of complications can be minimized, and many diabetic dogs can lead happy and fulfilling lives. Regular communication and collaboration with your veterinarian are crucial to address any potential risks or complications promptly.
What is the expected lifespan of a diabetic dog?
The expected lifespan of a diabetic dog can vary depending on various factors, including the dogs overall health, the success of diabetes management, the presence of other concurrent health conditions, and individual factors such as breed and genetics. With proper management and care, many diabetic dogs can live a happy and fulfilling life.
Generally, diabetic dogs can live for several years with appropriate treatment and monitoring. Some dogs may develop diabetes later in life and may already have underlying age-related health issues, which can impact their overall lifespan. However, with diligent management and regular veterinary care, it is possible to extend their lifespan and maintain their quality of life.
Its important to note that diabetes is a chronic condition that requires ongoing treatment and monitoring. Regular veterinary check-ups, blood glucose monitoring, insulin administration (if applicable), and adherence to the recommended treatment plan are crucial for managing diabetes effectively and maximizing your dogs lifespan.
Each dog is unique, and the prognosis can vary. Working closely with your veterinarian, following their recommendations, and maintaining open communication will help ensure the best possible outcome for your diabetic dog. They can provide more accurate insights into your dogs specific situation based on their individual health status and response to treatment.