Is sweet potato low GI

Heres What You Need to Know About Sweet Potatoes GI
Sweet potatoes get a lot of hype around the holidays, but theyre delicious and nutritious all year round. Packed with flavor and plenty of nutrients, sweet potatoes offer a wide array of health benefits. But did you know how we prepare them can actually affect their glycemic index? Not to worry! Theyre generally a medium glycemic index food, but if you need to keep your dishs glycemic index as low as possible, we know a few tricks to keep your sweet potato glycemic index on the down low.
What Is the Glycemic Index?
{{mid-cta}}
The glycemic index (GI) measures how carbohydrate-containing foods can affect your blood sugar levels. Measured on a scale of 0 to 100, foods can be classified as low, medium, and high-glycemic-index foods:
- Low-GI: 0-55
- Medium-GI: 56-69
- High-GI: 70-100
Simple carbs or foods with added sugars break down more quickly in the bloodstream, earning them a higher GI score. On the other hand, foods with high protein, fat, or fiber content will have less of an effect on our blood sugar levels and usually lower GI scores.
While a foods chemical makeup is largely responsible for its glycemic index, its preparation can also impact its GI value. Different cooking methods can alter the chemical structure of a food, ultimately influencing our glycemic response after consumption. This is especially true for sweet potatoes.
Glycemic Index of Sweet Potato
Cooking methods can have a significant impact on the glycemic index of the final dish. The glycemic index for sweet potatoes is no exception. Sweet potatoes can have a glycemic index between 44 and 91, depending on how they're prepared.
Boiling
When sweet potatoes are boiled, its thought that they retain more resistant starch, which helps resist digestion and limits its effects on blood sugar levels. The GI of a boiled sweet potato is 44, which tells us that boiled sweet potatoes can be an integral part of a low glycemic index meal.
Baking
Baked sweet potatoes have a significantly higher GI than sweet potatoes in any other form. In fact, when baked for 30 minutes, the baked sweet potato glycemic index falls around 91 on the GI scale, classifying them as high GI food.
Roasting
Similar to baking, roasting sweet potatoes will break down their resistant starch and increase their glycemic index. Remember, a high GI score can rapidly spike your blood sugar levels, so eat them in moderation.
Steaming
Steaming your sweet potatoes exposes them to less heat than baking them in an oven. When steamed for approximately 35 minutes, sweet potatoes have a glycemic index of 71 (which puts them right on the border between a medium and high GI).
Frying
Sweet potatoes that have been sliced and deep-fried in oil have a slightly lower GI than baked or roasted ones. With an average GI value of 58, they are classified as a medium GI food. The presence of fat can help slow the emptying of the stomach and the absorption of sugar in the bloodstream. So, instead of regular french fries that can have a GI of up to 76 and lack variety in micronutrients, you might opt for sweet potato fries!
Why Does Glycemic Index Vary With Cooking?
How foods are cooked can significantly impact their nutritional value and glycemic index, which is especially true for sweet potatoes. For instance, one cup of raw sweet potatoes contains approximately 114 calories, 26.7 grams of carbohydrates, and 5.6g of sugar. However, the nutrition facts shift slightly when the potato is exposed to heat. One cup of baked sweet potatoes contains approximately 180 calories, 41.4 g of carbs, and 13 g of sugar.
So why does cooking increase carbohydrates in sweet potatoes? When exposed to heat during the cooking process, the starch in sweet potatoes breaks down into two polysaccharides called amylopectin and amylose. Polysaccharides are carbohydrates made up of a number of sugar molecules, and our pancreatic enzymes can easily digest them. As they are digested, they turn into maltose, a sugar our body can use for energy, thus causing a spike in our blood sugar levels.
Simply put, once heat breaks down the starch in sweet potatoes, its easier for your body to convert it into sugar, thus affecting your blood sugar levels more immediately.
Are Sweet Potatoes Healthy?
The simple answer to that question is yes, absolutely! All foods can fit into a well-balanced diet, especially whole foods packed with tons of nutrients. Sweet potatoes are rich in:
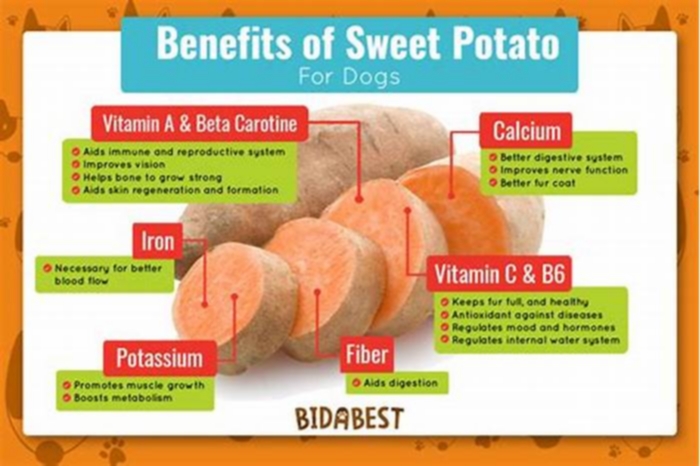
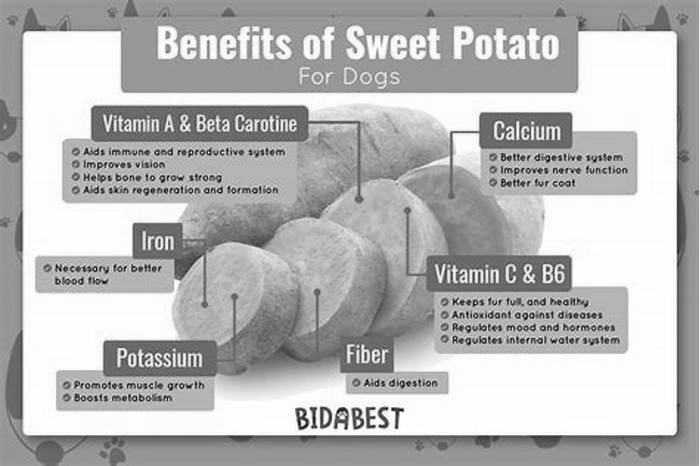
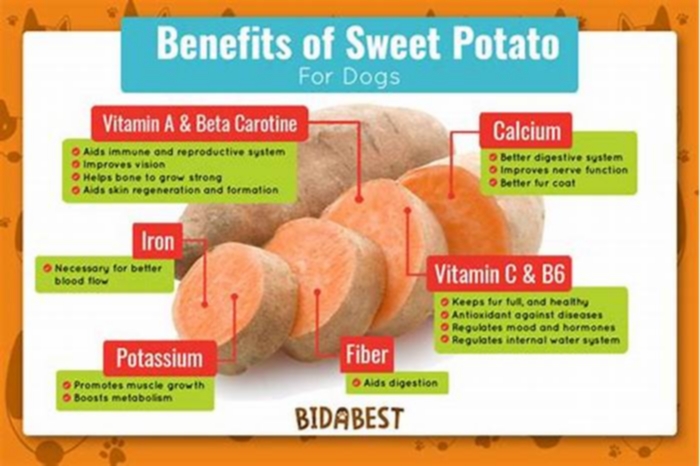
- Vitamin A in the form of beta carotene.
- Vitamin B6.
- Vitamin C.
- Potassium.
- Zinc.
- Magnesium.
- Fiber.
Sweet potatoes are also high in antioxidants called carotenoids, which gives sweet potatoes their orange color. Antioxidants can help protect our cells from day-to-day damage.
You might also wonder, are sweet potatoes good for diabetics? Again, yes, but we still need to be aware of our glycemic response. Even with all the health benefits that sweet potatoes offer, its important to be mindful of portion sizes and the timing of our meals. The glycemic index can be a helpful tool when navigating those aspects of our diet.
How to Avoid Blood Sugar Spikes
Sweet potatoes fall in the middle of the glycemic index, but dont let that deter you from adding them to the menu. There are a couple of things we can do to help manage our glycemic response when enjoying sweet potatoes:
Reduce Heat Exposure
The longer a sweet potato is exposed to heat, its GI will likely increase. Baking a sweet potato usually takes around 45 minutes of cooking time at high heat, but you can reduce heat exposure by trying different cooking methods, such as steaming or microwaving. Steaming only needs about 20 minutes to cook your sweet potato thoroughly. Or if you really want to cut down the heat exposure, microwaving your sweet potatoes only takes about 5 to 10 minutes.
Go for Lower-Indexed Sweet Potato Varieties
Did you know different sweet potato varieties have different GI values?
Orange Sweet Potatoes
Orange sweet potatoes tend to be the most common type found in U.S. grocery stores and restaurants. If youre considering the sweet potato vs white potato glycemic index, orange sweet potatoes have a higher fiber content and, thus, a lower glycemic index, making them a more nutritious option for those with diabetes.
Purple Sweet Potatoes
Purple sweet potatoes have a lower glycemic load than orange sweet potatoes. They contain anthocyanins, which give them their lavender hue inside and out. Research has shown that anthocyanins may help prevent and treat type 2 diabetes by improving insulin resistance.
Japanese Sweet Potatoes
Japanese sweet potatoes, sometimes called white sweet potatoes, contain the extract caiapo. Research has shown a connection between caiapo and reduced fasting and two-hour blood glucose levels.
3 Sweet Potato Recipe Ideas to Try Out
You might immediately think of Grandmas famous sweet potato casserole when you think of sweet potatoes. And while that is the MVP of every holiday dinner, wed be missing out if we didnt enjoy sweet potatoes in any of their other delicious forms.
Consider some of these fresh and savory recipes next time you want to add sweet potatoes to the menu:
Sweet Potato Nachos
Swap out those tortilla chips for thinly sliced sweet potatoes if you want to kick your favorite nacho dish up a notch. Just place your sweet potato slices evenly in the air fryer and spray with a nonstick cooking spray for a few seconds. Top with your favorite frozen veggies (and maybe a fresh jalapeo for taste) and spray again.
Air fry them at 375 degrees for about 20 minutes or until the potatoes are tender yet crisp. Top with cheese, cook for another two minutes, add your favorite garnishes, and theyre ready to eat!
Avocado and Sweet Potato Salad
If youre looking for a refreshing and satisfying meal, try throwing some roasted sweet potatoes and fresh avocados into your favorite salad. You wont be sorry you did! Toss them into a mixture of fresh greens and other veggies for a quick, nutrient-dense meal in minutes. Add chicken for a pop of protein or black beans if you follow a vegan diet.
Greens, Sweet Potatoes, and Egg Bowl
This breakfast bowl is packed with nutrients and can be enjoyed any time of the day. Cook your eggs to your liking and lay them atop a bed of fresh greens. Include roasted sweet potatoes, diced avocado, and cooked mushrooms to add more nutrients and fiber to this savory meal.
Monitoring a Healthy and Free Diet
Understanding a foods impact on blood glucose levels is key to choosing the right foods at the best times. Optimizing our glycemic response to meals helps us meet our immediate nutrition needs while keeping our long-term health in mind. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) makes that easier and more accessible than ever, and Signos is leading the way.
This wearable CGM connects via Bluetooth to the Signos app to provide real-time feedback for every meal. We all respond to foods differently, so access to our glucose data can be a real game changer. CGMs make optimizing our nutritional intake manageable, which helps us make small, sustainable changes to avoid blood glucose spikes. And we know controlled blood glucose levels ultimately help us prevent chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and obesity.
Sweet Potato Glycemic Index: Health Benefits
Sweet potatoes often are associated with the holidays and Thanksgiving meals. These tubular vegetables are packed with vitamins and minerals and come in various sizes and colors. While sweet potatoes are high in carbohydrates, they generally have a low glycemic index. They can benefit those living withtype 2 diabetesdue to their high levels of magnesium and fiber.
This article will dive deeper into how sweet potatoes may impact blood sugar levels and the health benefits of including this vegetable in your diet.
Get more information about weight loss, glucose monitors, and living a healthier life
Thank you! Your submission has been received!
Oops! Something went wrong while submitting the form.
Glycemic Index Table
There are several types of sweet potatoes, which all have varying glycemic index levels.
- Purple sweet potato: This sweet potatos color can be attributed to anthocyanins, packed with antioxidants. The glycemic index for this type of sweet potato is 77, which is considered high.
- Orange sweet potato:This sweet potato variety is filled with beta-carotene and has a glycemic index of 44 when boiled.
- Red sweet potato:This sweet potato has orange flesh and a red-copper skin color. The glycemic index of this variety is 84.
Thecooking methodof sweet potatoes also can change the glycemic index of the vegetable.
- Boiling:This preparation method can alter the chemical composition of the sweet potato and prevent spikes in blood sugar levels by allowing the starches to be easily digested. The time spent boiling sweet potatoes also makes a difference. When boiled for 30 minutes, sweet potatoes have a glycemic index of 46, but when boiled for eight minutes, the glycemic index rises to 61.
- Roasted: The roasting process destroys resistant starch, giving the sweet potato a higher glycemic index. Sweet potatoes that are peeled and roasted have a glycemic index of 82, a high glycemic index rating.
- Baked: Baked sweet potatoes also have a high glycemic index rating. Sweet potatoes that have been peeled and baked for 45 minutes have a glycemic index of 94, which is comparable to white rice and instant mashed potatoes.
- Fried: Surprisingly, fried sweet potatoes have a slightly lower glycemic index than roasted or baked versions because they contain fat, which slows glucose absorption (sugar). Sweet potatoes that have been peeled and fried in vegetable oil have a glycemic index of 76, comparable to cake, doughnuts, and jelly beans.
The below glycemic index and glycemic load data is for 100 grams of boiled orange sweet potatoes:
Glycemic Index
Serving Size
Carbohydrate* per Serving (g)
GL per Serving

Nutritional Facts
Sweet potatoes contain vitamins A, C, and manganese. They are also rich in potassium, fiber, and zinc. Sweet potatoes, especially the orange and purple varieties, contain abundant antioxidants that protect the human body against free radicals, which can damage DNA and trigger inflammation.
The nutritional information below is for 100 g of raw orange sweet potatoes.
Calories
Carbs
Protein
Fiber
Cholesterol
Vitamins
A (393.13 g), B12 (0.05 g), B6 (0.16 mg), C (5.45 mg), D (4.14 IU), Potassium (486 mg), Phosphorus (37 mg), Calcium (22 mg), Magnesium (19.1 mg)
Sodium
Total Fat
Health Benefits
Sweet potatoes are considered a superfood because of the numerous health benefits they are associated with. Lets take a look at some of these below.

Aids in Gut Health
Sweet potatoes contain both soluble and insolublefiber. The human body cannot digest these types of fiber, so they remain within the digestive tract and provide several gut-related benefits. Viscous fibers, a type of soluble fiber, absorb water and soften stool. Some soluble and insoluble fibers can be fermented by bacteria in your gut and create short-chain fatty acids that fuel the cells in the intestinal lining and keep this part of your body healthy.
Test-tube studies have found that purple sweet potatoes' antioxidants promote healthy gut bacteria growth, includingBifidobacteriumandLactobacillusspecies. Increased amounts of gut bacteria are associated with stronger gut health and a lower risk of conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
May Protect Against Cancer
Purple sweet potatoes contain anthocyanins, a group of antioxidants that have been shown to slow the growth of cancer cells in test-tube studies. The types of cancers observed in the studies included bladder, colon, stomach, and breast cancers.
Extracts of sweet potato peels have also been found to have anti-cancer properties in several test-tune and animal studies. However, studies have not used human subjects to verify these findings.
Supports Healthy Vision
Orange sweet potatoes contain high levels of beta-carotene, with one cup of baked orange sweet potatoes providing more than twice the daily recommended levels of beta-carotene for the average adult.
Beta carotene converts to vitamin A and forms light-detecting receptors in the human eye. Severe deficiencies of vitamin A can lead to xerophthalmia, a type of blindness. Eating foods rich in beta carotene, including sweet potatoes, may help prevent this condition.
Studies have also found that anthocyanins in purple sweet potatoes can protect cells in the eye from damage, which can boost overall eye health.
May Improve Brain Function
One study found that anthocyanins in purple sweet potatoes could help protect the brain by reducing inflammation and preventing damage from free radicals. Another study found that supplementing with purple sweet potato extract could reduce inflammation markers and improve spatial memory in mice.
Studies have not been performed with human participants, but as a general guideline, it has been shown that a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants is associated with a 13% lower risk of dementia.
Is Sweet Potato Good for Weight Loss?
Sweet potatoes may promote fullness and aid you in eating fewer calories, which can aid weight loss goals. Uncooked sweet potatoes are 77% water and 13% fiber, which can allow you to feel satiated without consuming a lot of calories.
One review that looked at 48 studies found thateating more fiberover one year was associated with sustained weight loss of at least 5% of the participants body weight.26 An eight-week study with 58 participants had similar findings.
If you want to incorporate sweet potatoes into your meals, here are some ideas to try:
- Swap out tortilla chips for thinly sliced sweet potatoes. Optional: use an air fryer instead of a deep fryer.
- Add sweet potatoes to a salad to any salad.
- Add sweet potatoes to a breakfast bowl full of vegetables and eggs.
Is Sweet Potato Safe for People Living with Diabetes?
Sweet potatoes are high in fiber and, depending on the variety and cooking method can have a low glycemic index. This will result in smaller spikes in blood sugar levels, which can help those living with diabetes stay within an optimal blood sugar range.
It is important to be mindful of serving size and cooking methods if you live with diabetes. Aim to consume boiled or steamed sweet potatoes. Baking, roasting, or frying sweet potatoes causes an increase in the vegetables glycemic index, which can lead to severe and sudden spikes in blood sugar levels.
Get more information about weight loss, glucose monitors, and living a healthier life
Thank you! Your submission has been received!
Oops! Something went wrong while submitting the form.
Allergies
Sweet potatoes are considered a low risk for food allergies.
Symptoms of a sweet potato allergy can include itchiness of the mouth, lips, or throat, swelling, and redness. In severe cases, allergic reactions can cause hives, difficulty breathing, and anaphylaxis. Please consult a healthcare professional if you suspect an allergy, sensitivity, or intolerance to sweet potatoes.