Is banana high glycemic
How Bananas Affect Diabetes and Blood Sugar Levels
If you have diabetes, bananas can be part of a healthy eating plan. Some tips may help reduce blood sugar spikes, including selecting an almost-ripe banana and eating it with other foods.
When you have diabetes, its important to keep your blood sugar levels as stable as possible.
Good blood sugar management can help prevent or slow the progression of some of the main medical complications of diabetes (
For this reason, its essential to avoid or minimize foods that cause blood sugar spikes.
Despite being a healthy fruit, bananas are pretty high in both carbs and sugar, which are the main nutrients that raise blood sugar levels.
This article investigates whether you can eat bananas if you have diabetes, as well as whether they affect your blood sugar.
If you have diabetes, being aware of the amount and type of carbs in your diet is important.
This is because carbs raise your blood sugar level more than other nutrients, which means they can greatly affect your blood sugar management.
When blood sugar levels rise in people without diabetes, their bodies produce insulin. This helps move sugar out of the blood and into cells, where its used or stored.
However, this process doesnt work as it should in people with diabetes. Instead, either the body doesnt produce enough insulin or the cells are resistant to the insulin that is made.
Without proper diabetes management, you may experience blood sugar spikes after eating high carb foods or have constantly high blood sugar levels, both of which are unhealthy.
How much sugar is in a banana?
One medium banana (about 126 grams) contains 29 grams of carbs and 112 calories. The carbs are in the form of sugar, starch, and fiber (
A medium banana contains about 15 grams of sugar (
SummaryBananas do contain simple carbs, which can cause blood sugar levels to rise more than other nutrients.
In addition to starch and sugar, a medium banana contains 3 grams of fiber (
Everyone, including people with diabetes, should try to eat enough dietary fiber because it has potential health benefits.
However, fiber is especially important for people with diabetes because it can help slow the digestion and absorption of carbs (
This can reduce blood sugar spikes and improve overall blood sugar management (
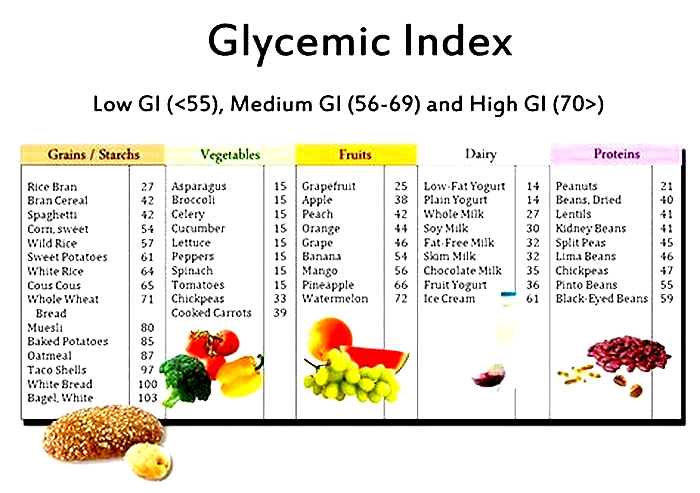
One way of determining how a carb-containing food will affect blood sugars is by looking at its glycemic index (GI).
The GI ranks foods based on how much and how quickly they raise blood sugar levels.
The scores run from 0100 with the following classifications:
- Low GI: 55 or less
- Medium GI: 5669
- High GI: 70100
Diets based on low GI foods are thought to be particularly good for people with type 2 diabetes (
This is because low GI foods are absorbed more slowly and cause a gradual rise in blood sugar levels rather than a large spike.
Overall, bananas score low to medium on the GI scale (4262, depending on the ripeness) (10).
SummaryIn addition to sugar and starch, bananas contain some fiber. This means the sugars in bananas are more slowly digested and absorbed, which could prevent blood sugar spikes.
The amount of this type of carbs in a banana varies depending on the ripeness.
Green, or unripe, bananas contain less sugar and more resistant starch (
Resistant starches are long chains of glucose (starch) that are resistant to digestion in the upper part of your digestive system (
This means they function similarly to fiber and wont cause a rise in blood sugar levels.
They also may help feed the friendly bacteria in your gut, which has been linked to improved metabolic health and better blood sugar management (
In fact, a 2015 study on blood sugar management in women with type 2 diabetes found some interesting results. In an 8-week period, those supplementing with resistant starch had better blood sugar management than those who didnt supplement (
Other studies have indicated that resistant starch may have beneficial effects for people with type 2 diabetes, such as improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation (
The role of resistant starch in type 1 diabetes is less clear.
A bananas effect on blood sugar depends on its ripeness
Yellow, or ripe, bananas contain less resistant starch than green bananas, as well as more sugar, which is more quickly absorbed than starch.
This means fully ripe bananas have a higher GI and will cause your blood sugar to rise faster than green unripe bananas (
SummaryGreen (unripe) bananas contain resistant starch, which doesnt raise blood sugar levels and may improve long-term blood sugar management. Yellow (ripe) bananas contain more sugar, so they may cause a bigger rise in blood sugar.
Discover more about Type 2 Diabetes
Ripeness isnt the only factor when it comes to the amount of sugar in your banana size also matters. The bigger the banana, the more carbs you will be getting.
This means a larger banana will have a greater effect on your blood sugar level. This portion-size effect is called the glycemic load.
Glycemic load is calculated by multiplying the GI of a food by the number of carbs in a serving and then dividing that number by 100.
A score of less than 10 is considered low, 1119 is medium, and 20 or more is high.
Bananas vary in size, from about 18.535 grams.
If a banana is fully ripe (with a GI of 62), then its glycemic load could range from 11 for a very small banana to 22 for a very large banana.
To ensure that your blood sugar doesnt rise too much, its important to be aware of the size of the banana youre eating.
SummaryThe size of the banana you eat determines its effect on your blood sugar level. The larger the banana, the more carbs youll consume and the greater the rise in your blood sugar will be.
Most general dietary guidelines for diabetes recommend following a healthy, balanced diet that includes fruit (
This is because eating fruits and vegetables has been linked to better health and a lower risk of conditions such as heart disease and some cancers (
People living with diabetes are at an even greater risk of these diseases, so eating enough fruits and vegetables is important (
Unlike refined sugar products such as candy and cake, the carbs in fruits like bananas come with fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
More specifically, bananas provide fiber, potassium, vitamin B6, and vitamin C. They also contain some antioxidants and beneficial plant compounds (
For most people with diabetes, fruits including bananas are a healthy choice.
However, some people who are following low carb diets need to watch their total carbohydrate intake to stay within their daily carb allotment. This means foods higher in carbs, including bananas, have to be limited on low carb diets.
If your doctor says you can eat bananas, its important to be mindful of the ripeness and size of a banana to reduce its effect on your blood sugar level.
SummaryFruits like bananas are healthy foods that contain fiber, vitamins, and minerals. You can include bananas in your diet even if you have diabetes. Check with your healthcare team before changing your eating plan.
If you have diabetes, its possible to enjoy fruit such as bananas as part of a healthy eating plan.
If you enjoy bananas, the following tips could help minimize their effects on your blood sugar levels:
- Watch your portion size. Eat a smaller banana to reduce the amount of sugar you eat in one sitting.
- Choose a firm, nearly ripe banana. Pick a banana thats not overly ripe so that the sugar content is slightly lower.
- Spread your fruit intake throughout the day. Spread out your fruit intake to help reduce the glycemic load and keep your blood sugar levels stable.
- Eat them with other foods. Enjoy your bananas with other foods, such as nuts or full fat yogurt, to help slow the digestion and absorption of the sugar.
If you have diabetes, remember that carb-containing foods can affect peoples blood sugars differently.
Therefore, you might want to monitor how eating bananas affects your blood sugar and adjust your eating habits accordingly.
Glycemic Index of Bananas: Impact on Your Blood Sugar Levels
Bananas are a nutritious and delicious fruit, rich in vitamin C, potassium, vitamin B6, manganese, magnesium, and fiber. Still, while this healthy fruit offers many potential health benefits, it can cause blood sugar spikes if eaten in excess.
Maximizing their benefits often means eating bananas in moderation. In this article, well explain the science behind bananas and their glycemic index. And well discuss ways to incorporate them into a healthy diet, not just for diabetes management but for overall health.
First Things First: What Is the Glycemic Index?
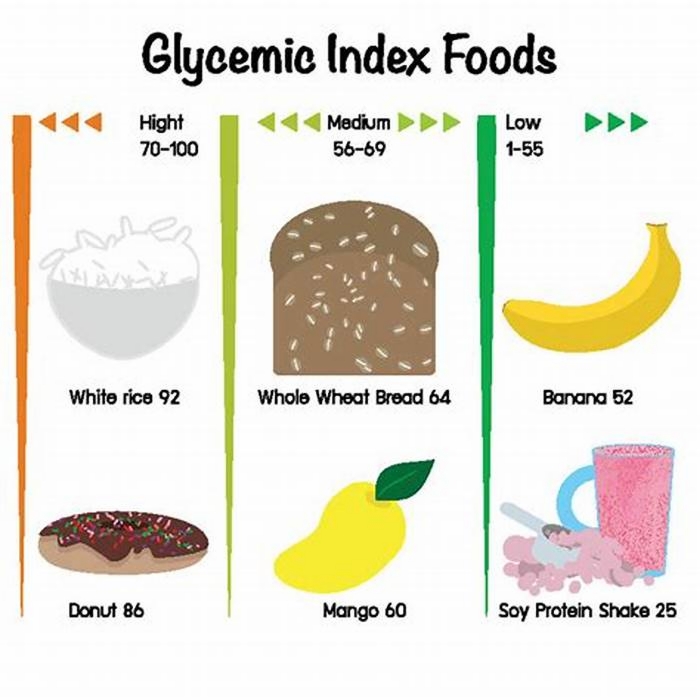
The glycemic index (GI) assigns a number to a food based on how quickly it can raise your blood glucose levels. These carbohydrate-containing foods are ranked on a scale of 0 to 100 and divided into low, medium, and high-glycemic categories:
- High-glycemic index foods = GI score of 70100
- Medium-glycemic index foods = GI score of 5069
- Low-glycemic index foods = GI score of 20-49
While a foods glycemic index is primarily predetermined by its carbohydrate content, it can also be affected by processing and cooking methods. For example, minimally processed whole grains typically have lower GI values than refined grains. If a carbohydrate requires cooking, the temperature, duration of cooking, and cooling and reheating can all affect its GI score.
{{mid-cta}}
Glycemic Index of Bananas
Do bananas raise blood sugar? You bet! But thats why we eat them. They are a carbohydrate source, meaning they provide us with energy as our bodies digest them. The trick is to understand how our bodies respond to their glycemic index.
So, how fast will a banana raise blood sugar? Bananas have an average glycemic index of 50, making them a medium-glycemic index food.1 However, a bananas GI score can vary depending on multiple factors.
For example, its ripeness will determine how much sugar is in a banana and its GI score. Generally, the more ripe a banana is, the higher its GI value will be. Also, portion size determines how many grams of carbohydrates you consume or the foods glycemic load. The larger your portion size, the more grams of carbs youll eat.
Why Does Glycemic Index Vary With Ripeness?
Amazingly, a bananas glucose levels will increase as the fruit ripens, changing its GI score throughout the process. At the start, green, unripe bananas contain resistant starch and less sugar than ripe bananas. Resistant starches are long chains of glucose that act similarly to fiber. This type of carbohydrate is resistant to digestion in the small intestine, meaning less glucose will be released into the bloodstream.
For this reason, unripe bananas are less likely to cause a rise in your blood sugar levels.2 In addition, resistant starches may also feed the friendly bacteria in your gut, which has been linked to improved blood sugar management.3
As bananas ripen, they turn yellow. This indicates that they have less resistant starch and more sugar, which will cause your blood glucose levels to rise faster. Therefore, their glycemic index increases as bananas ripen, giving them a higher GI value than unripe bananas.
Green
If you want a banana in its lowest GI form, go for an unripe, green banana. Green bananas typically have a GI score lower than the average 50.
Yellow
As a banana turns yellow, its glucose content increases. With more glucose, its more likely to cause an increase in your blood sugar, thus giving it a higher GI score than the average 50.
Spotted (Ripe)
Last but not least, fully ripened bananas have the highest GI score of all the stages. You often see recipes like banana bread that call for spotted bananas. This is because they have more glucose and a much sweeter taste. Fully ripe bananas can have a high GI, even up to a score of 75.
Are Bananas Considered Healthy?
Bananas can be a nutritious part of a well-balanced diet. However, be aware of the bananas ripeness and portion sizes to avoid spiking your blood sugar levels.
The carbs in a banana can also provide energy, but too much at once can send your sugar levels over the edge. Since unripe bananas are considered a low-GI food, they can be a great way to incorporate more nutrients into your meals without significantly affecting blood glucose.
To enjoy bananas with your overall health in mind, monitor your portion sizes and remember that other parts of your meal may also affect your blood glucose.
You can also incorporate different types of bananas to adjust your carbohydrate intake, but consider these tips:
Choose Yellow and Firm Bananas
Look for bananas that are yellow and have a firm feel. The banana will be firm if the fruits resistant starches are intact. As the resistant starches break down and glucose content increases, the banana will get softer and mushier.
Choose Smaller Bananas
Choosing a small banana can help reduce the number of carbs you consume. However, if you cant find a small or medium-sized banana, break a large banana in half and share the other half with a friend.
Eat Them in Moderation
Moderation is the name of the game when it comes to well-balanced nutrition. The same goes for your banana intake. Eating bananas in moderation, whether through portion sizes or frequency, can help you capitalize on their health benefits while maintaining balanced blood sugars.
Combine With Other Foods
Eating bananas with other foods gives your body other macronutrients to digest, helping to avoid blood sugar spikes that might occur if eating bananas alone. Foods like nuts, oats, and yogurt are rich in protein and healthy fats and pair well with bananas.
Bananas vs. Apples
All foods can fit into a well-balanced diet, including apples and bananas. In fact, including various fruits can help you meet your nutrition needs on both the macro and micronutrient levels because each food has its unique nutrition profile.
Apples and bananas provide very similar nutrition.One medium apple contains around 104 calories and 27 grams of carbs, whereas one medium banana contains 29 grams of carbs and about 112 calories.4,5 They also contain 3-4 grams of dietary fiber and a decent amount of vitamin C. However, apples have a notable amount of antioxidants, and bananas are rich in potassium.
3 Healthy Banana Recipe Ideas to Try
Bananas can add a boost of nutrients and flavor to a variety of recipes. Try some of these delicious recipes next time you want to incorporate bananas into your meals.
Banana Bread Casserole
For this recipe, youll need ripe bananas, thick slices of bread, eggs, water, and milk. Mix torn bread with slices of bananas in an oven-safe baking dish. Then, in a separate mixing bowl, beat your eggs, milk, and water. Add brown sugar to taste if desired.
Pour the mixture over the bread in your baking dish, and bake at 350 degrees until golden brown. You can serve it with vanilla yogurt on top or eat it on its own.
Banana Pancakes
Spice up your favorite pancake recipe by adding bananas to the mix. You can mash the bananas and stir them directly into the pancake mix or slice them up and add them to the pancakes as you pour the mixture into the skillet. The bananas will add delicious flavor and nutrients to your breakfast menu!
Green Banana Smoothie
Bananas can make a great addition to your favorite protein smoothie recipes. Consider looking for protein powders low in carbs, so you can add bananas for taste and texture without overdoing it on the carbs. By adding bananas, your carb intake comes from natural sugars versus added sugars from a high-carbohydrate protein powder.
I like to use a vanilla protein powder blended in almond milk with one-half banana, a large handful of spinach (or another leafy green veggie), and a tablespoon of peanut butter. The smoothie has a delicious flavor and a beautiful green hue. Because bananas contain fiber, they can increase your satiety, making that protein smoothie even more nutritious.
Learn How to Improve Your Nutrition and Monitor Your Glucose Levels with Signos Expert Advice
Signos continuous glucose monitoring can improve your health by helping you keep track of your diet and its effects on your blood sugar levels. Understanding our blood sugar response to food isnt just for those with type 2 diabetes. Our blood sugar levels affect heart disease, weight loss, kidney function, and skin health.
Signos gives us real-time data, showing how our bodies respond to the food we eat. By knowing how our body is affected by the carbohydrate content of our diets, we can develop well-balanced eating habits that serve our overall health well.
Find out if Signos is a good fit by taking a quick quiz! And if you have questions about your individualized nutrition needs, consider meeting with a registered dietitian!