Are eggs high in glycemic

Are Eggs Good for Diabetes? Glycemic Index, Sugar, and More
Are eggs good for diabetes? This question often takes center stage in the diabetes discussion.
In recent years, researchers have managed to shed light on the relationship between eggs and diabetes, particularly focusing on aspects such as glycemic index and sugar content. This article provides a clear understanding of the impact of eggs on diabetes and answers questions like Do eggs spike insulin? and Can diabetics eat eggs?.
Eggs: Nutritional facts
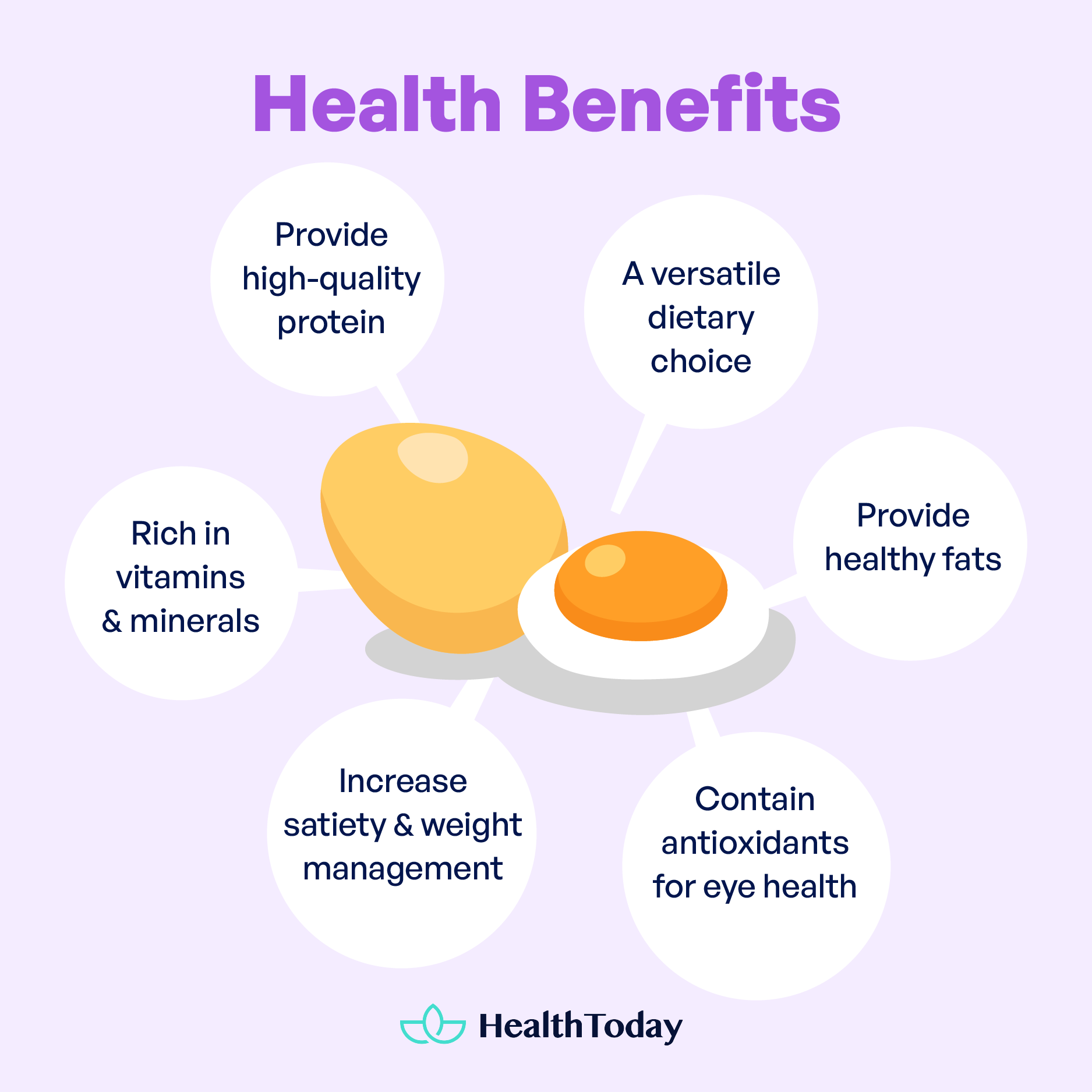
Eggs are a dietary staple, a versatile food source that complements different dietary goals; theyre good for blood sugar management, protein intake, and overall nutrient enhancement (1).
Glycemic index of eggs
Eggs have a glycemic index of 0 (2, 3) because of low carbohydrate (sugar) content. Thus, they have a slight impact on blood sugar levels (3), making them suitable for people with diabetes and their carbohydrate intake. Eggs dont cause a significant increase in blood glucose levels, even when you eat many (3).
Do eggs have sugar?
Eggs contain almost no sugar, which contributes to their low glycemic index. A 100 g whole hard-boiled egg contains 1.12 g of sugar (4). Among fructose, lactose, maltose, and galactose, glucose is the main free sugar found in eggs (5). Thus, eggs become an excellent choice for people who want to control their sugar intake.
Benefits
Eggs contain high-quality protein, and essential amino acids, which are needed for bodily functions (6, 7). They are also rich in vitamins and minerals such as vitamin D, B vitamins, selenium, and choline, which help improve brain health (8, 9, 10, 11).
Eating eggs also helps increase satiety and promote weight management because of their high protein content. So its best to include eggs in your meal plan (12).
Eggs also contain antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin (13), which have been shown to be good for eye health (14, 15, 16). Healthy fat in eggs contributes to improving overall health (8).
Whether youre following a low-glycemic diet, focusing on protein-rich foods, or striving to enhance nutrient intake, eggs are versatile and a great choice. The minimal effect on blood sugar, combined with the wide array of nutrients, makes eggs a cornerstone of a balanced and health-conscious diet.
Eggs and diabetes: Are they okay for diabetics?
Individuals with diabetes often wonder if eggs are a suitable addition to their diet. The question of Are eggs good for diabetes? remains a concern despite the health benefits that they offer.
Do eggs raise blood sugar and insulin?
The protein and healthy fats in eggs may help regulate insulin response (17). However, individual responses can vary.
Its advisable for individuals with diabetes to work with a healthcare professional or dietitian to create a well-balanced meal plan that aligns with specific health needs and goals. Eggs seem to be well-tolerated by many diabetics; people with diabetes should consider their condition and determine their optimal consumption.
Eggs and diabetes type 2
The research on questions, Are eggs OK for diabetics? or Are they indeed beneficial? remains a topic of interest. The effects of eggs on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity affect diabetes management and blood sugar control.
Studies suggest that eggs may not only be safe but also offer potential benefits for managing diabetes type 2 (18, 19, 20, 21). The protein and healthy fat content of eggs may also help improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism and contribute positively to blood sugar control (22)
Other studies suggest that eggs have limited effects on people with diabetes and insulin resistance (23, 24). However, other studies suggest daily egg consumption is associated with an increased risk of diabetes (25, 26).
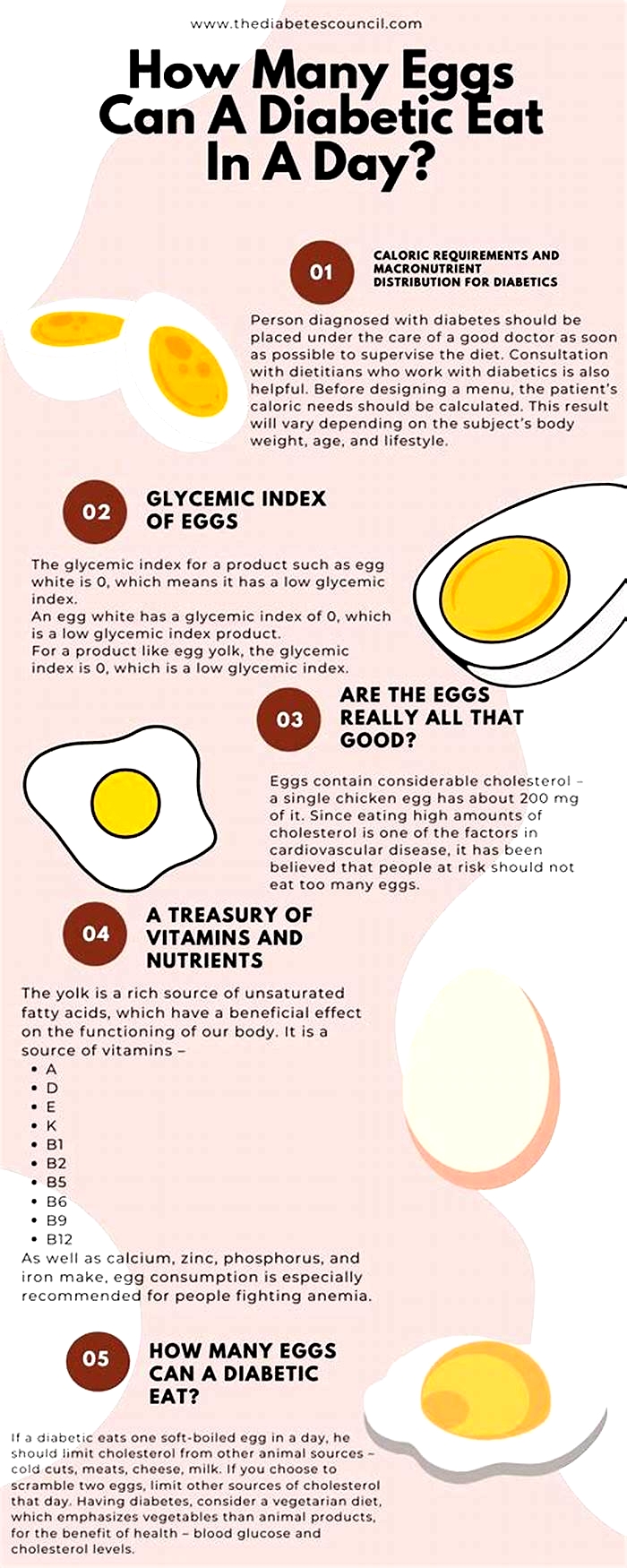
How many eggs can a diabetic eat in a day?
The number of eggs that people with diabetes can safely consume is a concern for people with diabetes because diabetes management requires a balance between nutritional needs and dietary restrictions. Individual factors such as overall dietary patterns, blood sugar control goals, and existing health conditions will affect your optimal egg intake.
Eggs dont cause a significant rise in blood sugar, but portion control remains important. People with diabetes can enjoy several eggs per week, up to two eggs per day, depending on individual conditions. Its recommended to include eggs with various foods to ensure a balanced and nutrient-rich diet.
How should diabetics eat eggs for breakfast?
Eggs can provide a satisfying and healthy start to the day, but how can diabetics make the most of their egg-based breakfast options while keeping blood sugar in check? Lets find out the answers!
Are hard-boiled eggs good for diabetics?
Boiled eggs emerge as an excellent breakfast choice for people with diabetes. The hard-boiled egg doesnt need added fats and ensures a low-calorie and low-carb option that helps keep blood sugar stable. Besides, their convenience and portability make them an excellent choice for busy mornings or as a nutritional snack throughout the day.
People with diabetes might ask, How many hard-boiled eggs can a diabetic eat? An appropriate portion of hard-boiled eggs hinges on individual factors such as nutritional needs, activity levels, and blood sugar goals. Including one or two hard-boiled eggs in breakfast can be a good approach (27), especially when combined with fiber-rich foods like vegetables or whole grains.
Poached and scrambled eggs can be good options when prepared without excessive fats and with healthy oils. Including vegetables in scrambled eggs adds fiber and nutrients, which might improve glycemic control.
You should consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to have the best-personalized guidance on egg intake and ensure a balanced and diabetes-friendly breakfast.
Can diabetics eat bacon and eggs?
Bacon and eggs are a classic breakfast duo, and its compatibility with diabetes management is worth trying. Bacon is high in saturated fats and sodium, which may impact heart health (28). Moreover, people with diabetes are at an increased risk of heart disease, which could worsen their diabetes. (29).
The question, Can diabetics eat eggs and cheese together? arises among other concerns for people who manage diabetes. Eggs and cheese can be part of a wholesome breakfast, but mindful portioning is advised because of the fat and calories from cheese. Opting for low-fat cheese varieties can help create a satisfying yet diabetes-friendly breakfast.
Recommended recipes with eggs
Eggs are a fantastic source of high-quality proteins and nutrients while being relatively low in carbs, which is a diabetes-friendly choice. We have collected some recipes below that can satisfy your egg cravings while still keeping your blood sugar levels stable and supporting your well-being.

Avocado-Eggs Toast
A whole-grain bread layered with avocados and egg on top can be a good option to start your day. This simple recipe cant go wrong and will provide you with essential nutrients. This dish is a symphony of flavors, merging the creamy avocados and eggs. You can be really creative by adding things like tomato or salmon to level up your simple bread.
Go to the recipe
Poached Eggs Salmon
Poached eggs and the smoked salmon combination might offer you an amazing taste. Whether its a perfect brunch or a simple breakfast, this dish will offer you a great dining experience and provide the proteins you need to maintain overall health.
Go to the recipe
Masala Omelette
Youre not a fan of toast but omelettes? Then you might want to try this vegetable omelet. It is a vibrant and satisfying combination of eggs, vegetables, and flavorful spices. Masala Omelette celebrates the magic of spices and the art of perfecting an egg-centric delight.
Go to the recipe
Silky Egg Curry
This recipe is a harmonious fusion of flavors, where the velvety eggs meet aromatic spices, creating a full of flavors that are nothing short of enchanting. With every bite, youll be amazed by the rich and luxurious texture of the curry as it delicately envelopes the eggs.
Go the the recipe
Crust-Free Ham and Asparagus
Enjoy the rich flavors of quiche with our ham and asparagus quiche. Although this recipe takes out the crust, the rich flavor of quiche with ham doesnt change. With each forkful, youll savor a harmony of textures of tender asparagus, savory ham, and the creamy eggs that melt in your mouth. Its a perfect Sunday brunch dish!
Go to the recipe
Do eggs have carbs or sugar?
Eggs are low in carbohydrates and sugar. They are primarily comprised of protein and healthy fats. A typical large egg contains less than one gram of carbohydrates, which makes eggs a good choice for people who are managing their carbohydrate intake.
Can diabetics eat deviled eggs?
Yes, diabetics can generally enjoy deviled eggs as part of their diet. Deviled eggs are made from hard-boiled eggs filled with a mixture of mayonnaise and seasonings. However, its important to be mindful of portion sizes and ingredients used, as it may be high in fat.
Can a diabetic patient eat egg yolk?
Yes, people with diabetes can definitely eat egg yolks. Egg yolks are a good source of various nutrients, including essential vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. They dont significantly impact blood sugar levels, as they contain minimal carbohydrates. But portion control and overall dietary balance are also important.
Are eggs good for prediabetes?
Yes, eggs can be a good food choice for individuals with prediabetes because of their low carbohydrate content. They are rich in high-quality protein and healthy fats, which keep you full longer and stabilize blood sugar. Including eggs in a balanced diet for prediabetes can provide essential nutrients and support overall health.
Can diabetics eat 2 eggs a day?
Yes, people with diabetes can safely consume up to 2 eggs a day. Eggs are a nutritious source of nutrients and have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Individuals dietary needs can be varied; its important to consider other aspects of your diet, such as carbohydrate intake and overall calorie consumption.
Summary
In a nutshell, can diabetics eat eggs? Yes, owing to their low glycemic, high protein, and healthy fat content. Some research shows eggs have a positive impact on diabetes management, while others show zero to negative impact on people with diabetes.
Eggs have minimal impact on blood sugar levels and can support overall health. Diabetics can safely eat up to two eggs per day on a regular basis, but they should consult with their nutritionist.
How Do You Feel About This Article?
What are high and low glycemic index foods?
Foods with a high glycemic index (GI) raise blood sugar quickly and may cause health issues if someone eats too many of them.
Eating a low GI diet may help to prevent and manage diabetes and cardiovascular disease. A person may also manage their weight with a low GI diet as part of an overall healthful eating approach.
This article explains what the GI is, and which foods are high and low GI items. It also outlines the benefits of a low GI diet and gives an example of a low GI meal plan.
The glycemic index (GI) is a measurement that ranks foods containing carbohydrates according to how much they affect someones blood sugar. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) rank foods from 1100 and use pure glucose, with a GI of 100, as a reference.
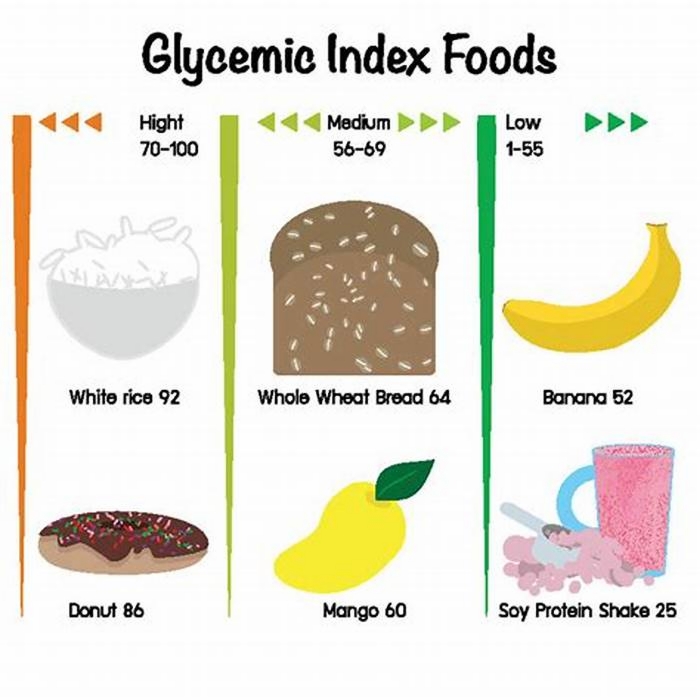
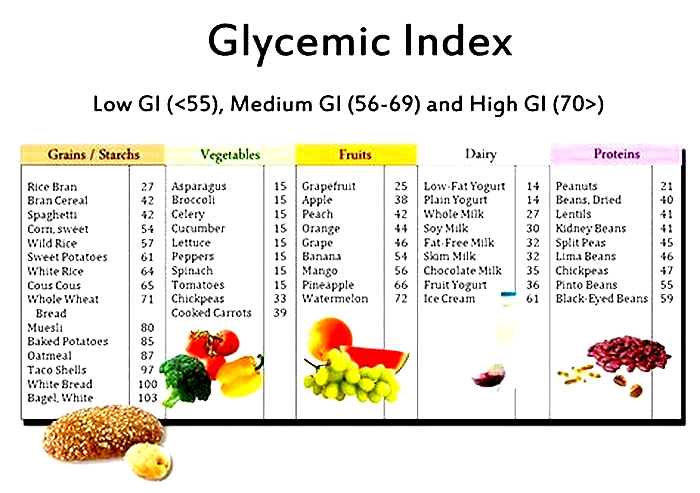
The Glycemic Index Foundation (GIF) classify the GI of foods as either low, medium, or high:
- low GI is 55 or less
- medium GI is 5669
- high GI is 70 or greater
The American Diabetes Association provide a list of common foods and their GI. They note that some sources use white bread as a reference point instead of pure glucose.
Glycemic load (GL) is another measurement that some experts believe gives a more realistic picture of how foods affect blood sugar. GL considers the amount of carbohydrate in a portion of food, as well as its GI.
People can use the glycemic index to help them choose healthful foods and monitor how much sugar and carbohydrates they eat. This approach can help someone manage their weight or a health condition such as diabetes.
The GIF explain that several factors influence how fast a particular food raises someones blood sugar. These factors can include:
- how refined the carbohydrate is
- the physical and chemical structure of the food
- the cooking method
- how much fiber the food contains
- how much protein, fat, and acid the food contains
Generally speaking, refined and processed carbohydrates metabolize into glucose more quickly. Foods with fiber, protein, and fats release glucose more slowly, so they have a lower GI. Longer cooking times can break foods down, which means that someone consuming those foods absorbs glucose quicker.
Someone who wants to manage their weight or diabetes can find out the GI of foods from the International Tables of Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load Values. According to the table, the following foods are high in GI:
- white and whole wheat bread
- white rice
- breakfast cereals and cereal bars
- cakes, cookies, and sweet treats
- potatoes and fries
- chips and rice crackers
- fruits such as watermelon and pineapple
- sweetened dairy products such as fruit yogurts
People following a low GI diet can eat foods with a medium GI of 5669, but less frequently than low GI foods. Food with a medium GI includes rye bread and raisin bran cereal.
High GI foods tend to spike a persons blood sugar, causing their body to produce more
Besides those short-term effects, dysregulated blood glucose can have longer-term health effects such as insulin resistance and diabetes.
According to the International Carbohydrate Quality Consortium (ICQC), there is a consensus that diets low in GI and GL are relevant to the prevention and management of diabetes, coronary heart disease, cancer, and probably obesity.
Research suggests that a low GI diet may be beneficial and help prevent some health issues.
Being aware of the GI of foods may help people control their blood sugar and prevent or delay complications relating to diabetes.
A
A low GI diet may also help with gestational diabetes. This is a condition where someone develops high blood sugar while pregnant, which usually resolves after they give birth.
A
A
High GI foods may also affect mood and energy. A
A
The following are examples of meal options for someone following a low GI meal plan:
Breakfast options
Some low GI breakfast options may include:
- scrambled eggs with smoked salmon
- buckwheat pancakes with berries
- breakfast quesadillas with black beans, spinach, and mushrooms
Lunch options
Low GI lunch options can include:
- black bean soup
- mango chicken and almond on rye bread
- cauliflower and celeriac soup
Dinner options
Low GI dinner options can include:
- lamb shanks with barley, garden peas, and mint
- Tex-Mex tofu soft tacos
- Indian-style spiced vegetable and cheese parcels
Snack options
Low GI snack options can include:
- a slice of cinnamon, oat, and almond loaf
- homemade full-of-fruit muffins
- roasted soy nuts
When planning meals it may prove useful to count carbs. By managing carbs using the GI, people may be able to
A person may find following a low GI diet somewhat complicated. A person needs to know the GI of all the foods on their plate, which can prove problematic when a meal has many ingredients. Following a low GI diet can limit what options someone has when eating out in restaurants.
A person also needs to consider the amount of fiber, fats, and protein in a meal to see how much the meal as a whole may affect their blood glucose.
A 2015 study advises that people need to consider low GL and GI in the context of overall healthful eating. According to a
Therefore it may be more important for people to be conscious of the GI of foods while maintaining a balanced and healthful diet.
A person may want to follow a low GI diet to manage their weight or health condition. To do so, they can find out the GI of foods and make a meal plan. A person should also consider other aspects of a balanced and healthful diet, such as fiber and whole grains, in that planning.
Low GI diets may be beneficial for preventing and managing insulin resistance, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Planning a low GI diet is potentially complex, however, so a person might consider enlisting the advice of a registered dietitian.